Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system.
Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices add to greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.

Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to thawing permafrost, retreat of glaciers and sea ice decline. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimise future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise.
Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization (WHO) calls climate change the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change.
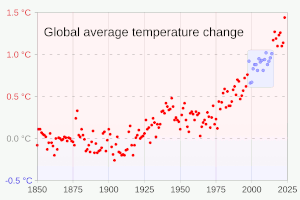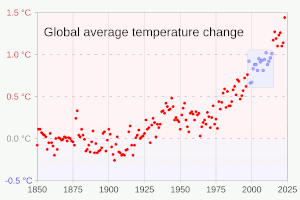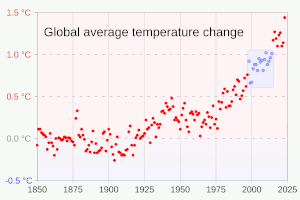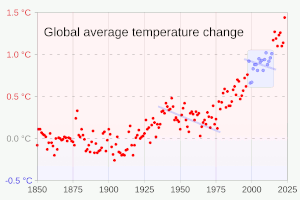
Many climate change impacts have been felt in recent years, with 2023 the warmest on record at +1.48 °C (2.66 °F) since regular tracking began in 1850. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as melting all of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.7 °C (4.9 °F) by the end of the century. Limiting warming to 1.5 °C will require halving emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
Fossil fuel use can be phased out by conserving energy and switching to energy sources that do not produce significant carbon pollution. These energy sources include wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear power. Cleanly generated electricity can replace fossil fuels for powering transportation, heating buildings, and running industrial processes. Carbon can also be removed from the atmosphere, for instance by increasing forest cover and farming with methods that capture carbon in soil.
Terminology
Before the 1980s it was unclear whether the warming effect of increased greenhouse gases was stronger than the cooling effect of airborne particulates in air pollution. Scientists used the term inadvertent climate modification to refer to human impacts on the climate at this time. In the 1980s, the terms global warming and climate change became more common, often being used interchangeably. Scientifically, global warming refers only to increased surface warming, while climate change describes both global warming and its effects on Earth's climate system, such as precipitation changes.
Climate change can also be used more broadly to include changes to the climate that have happened throughout Earth's history. Global warming—used as early as 1975—became the more popular term after NASA climate scientist James Hansen used it in his 1988 testimony in the U.S. Senate. Since the 2000s, climate change has increased usage. Various scientists, politicians and media now use the terms climate crisis or climate emergency to talk about climate change, and global heating instead of global warming.
Global temperature rise

Temperature records prior to global warming
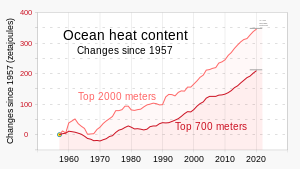
Over the last few million years Human beings evolved in a climate that cycled through ice ages, with global average temperature ranging between 1 °C warmer and 5–6 °C colder than current levels. One of the hotter periods was the Last Interglacial between 115,000 and 130,000 years ago, when sea levels were up to 6 to 9 meters higher than today. The most recent glacial maximum 20,000 years ago had sea levels that were about 125 meters (410 ft) lower than today. The warming period which followed included a pulse of warming when sea levels rose 18 meters (59 ft) over a period of 500 years.
Temperatures stabilized in the current interglacial period beginning 11,700 years ago. Historical patterns of warming and cooling, like the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age, did not occur at the same time across different regions. Temperatures may have reached as high as those of the late 20th century in a limited set of regions. Climate information for that period comes from climate proxies, such as trees and ice cores.
Warming since the Industrial Revolution

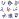
Around 1850 thermometer records began to provide global coverage. Between the 18th century and 1970 there was little net warming, as the warming impact of greenhouse gas emissions was offset by cooling from sulfur dioxide emissions. Sulfur dioxide causes acid rain, but it also produces sulfate aerosols in the atmosphere, which reflect sunlight and cause so-called global dimming. After 1970, the increasing accumulation of greenhouse gases and controls on sulfur pollution led to a marked increase in temperature.
Multiple independent datasets all show worldwide increases in surface temperature, at a rate of around 0.2 °C per decade. The 2013-2022 decade warmed to an average 1.15 °C [1.00–1.25 °C] compared to the pre-industrial baseline (1850–1900). Not every single year was warmer than the last: internal climate variability processes can make any year 0.2 °C warmer or colder than the average. From 1998 to 2013, negative phases of two such processes, Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) caused a so-called "global warming hiatus". After the hiatus, the opposite occurred, with years like 2023 exhibiting temperatures well above even the recent average. This is why the temperature change is defined in terms of a 20-year average, which minimises the noise of hot and cold years and decadal climate patterns, and detects the long-term signal.: 5
A wide range of other observations reinforce the evidence of warming. The upper atmosphere is cooling, because greenhouse gases are trapping heat near the Earth's surface, and so less heat is radiating into space. Warming reduces average snow cover and forces the retreat of glaciers. At the same time, warming also causes greater evaporation from the oceans, leading to more atmospheric humidity, more and heavier precipitation. Plants are flowering earlier in spring, and thousands of animal species have been permanently moving to cooler areas.
Differences by region
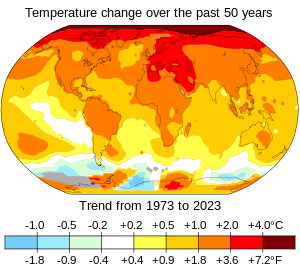
Different regions of the world warm at different rates. The pattern is independent of where greenhouse gases are emitted, because the gases persist long enough to diffuse across the planet. Since the pre-industrial period, the average surface temperature over land regions has increased almost twice as fast as the global average surface temperature. This is because oceans lose more heat by evaporation and oceans can store a lot of heat. The thermal energy in the global climate system has grown with only brief pauses since at least 1970, and over 90% of this extra energy has been stored in the ocean. The rest has heated the atmosphere, melted ice, and warmed the continents.
The Northern Hemisphere and the North Pole have warmed much faster than the South Pole and Southern Hemisphere. The Northern Hemisphere not only has much more land, but also more seasonal snow cover and sea ice. As these surfaces flip from reflecting a lot of light to being dark after the ice has melted, they start absorbing more heat. Local black carbon deposits on snow and ice also contribute to Arctic warming. Arctic surface temperatures are increasing between three and four times faster than in the rest of the world. Melting of ice sheets near the poles weakens both the Atlantic and the Antarctic limb of thermohaline circulation, which further changes the distribution of heat and precipitation around the globe.
Future global temperatures

The World Meteorological Organization estimates a 66% chance of global temperatures exceeding 1.5 °C warming from the preindustrial baseline for at least one year between 2023 and 2027. Because the IPCC uses a 20-year average to define global temperature changes, a single year exceeding 1.5 °C does not break the limit.
The IPCC expects the 20-year average global temperature to exceed +1.5 °C in the early 2030s. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (2023) included projections that by 2100 global warming is very likely to reach 1.0-1.8 °C under a scenario with very low emissions of greenhouse gases, 2.1-3.5 °C under an intermediate emissions scenario, or 3.3-5.7 °C under a very high emissions scenario. In the intermediate and high emission scenarios, the warming will continue past 2100.
The remaining carbon budget for staying beneath certain temperature increases is determined by modelling the carbon cycle and climate sensitivity to greenhouse gases. According to the IPCC, global warming can be kept below 1.5 °C with a two-thirds chance if emissions after 2018 do not exceed 420 or 570 gigatonnes of CO2. This corresponds to 10 to 13 years of current emissions. There are high uncertainties about the budget. For instance, it may be 100 gigatonnes of CO2 equivalent smaller due to CO2 and methane release from permafrost and wetlands. However, it is clear that fossil fuel resources need to be proactively kept in the ground to prevent substantial warming. Otherwise, their shortages would not occur until the emissions have already locked in significant long-term impacts.
Causes of recent global temperature rise

The climate system experiences various cycles on its own which can last for years, decades or even centuries. For example, El Niño events cause short-term spikes in surface temperature while La Niña events cause short term cooling. Their relative frequency can affect global temperature trends on a decadal timescale. Other changes are caused by an imbalance of energy from external forcings. Examples of these include changes in the concentrations of greenhouse gases, solar luminosity, volcanic eruptions, and variations in the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
To determine the human contribution to climate change, unique "fingerprints" for all potential causes are developed and compared with both observed patterns and known internal climate variability. For example, solar forcing—whose fingerprint involves warming the entire atmosphere—is ruled out because only the lower atmosphere has warmed. Atmospheric aerosols produce a smaller, cooling effect. Other drivers, such as changes in albedo, are less impactful.
Greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases are transparent to sunlight, and thus allow it to pass through the atmosphere to heat the Earth's surface. The Earth radiates it as heat, and greenhouse gases absorb a portion of it. This absorption slows the rate at which heat escapes into space, trapping heat near the Earth's surface and warming it over time.
While water vapour (≈50%) and clouds (≈25%) are the biggest contributors to the greenhouse effect, they primarily change as a function of temperature and are therefore mostly considered to be feedbacks that change climate sensitivity. On the other hand, concentrations of gases such as CO2 (≈20%), tropospheric ozone, CFCs and nitrous oxide are added or removed independently from temperature, and are therefore considered to be external forcings that change global temperatures.
Before the Industrial Revolution, naturally-occurring amounts of greenhouse gases caused the air near the surface to be about 33 °C warmer than it would have been in their absence. Human activity since the Industrial Revolution, mainly extracting and burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, resulting in a radiative imbalance. In 2019, the concentrations of CO2 and methane had increased by about 48% and 160%, respectively, since 1750. These CO2 levels are higher than they have been at any time during the last 2 million years. Concentrations of methane are far higher than they were over the last 800,000 years.

Global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in 2019 were equivalent to 59 billion tonnes of CO2. Of these emissions, 75% was CO2, 18% was methane, 4% was nitrous oxide, and 2% was fluorinated gases. CO2 emissions primarily come from burning fossil fuels to provide energy for transport, manufacturing, heating, and electricity. Additional CO2 emissions come from deforestation and industrial processes, which include the CO2 released by the chemical reactions for making cement, steel, aluminum, and fertiliser. Methane emissions come from livestock, manure, rice cultivation, landfills, wastewater, and coal mining, as well as oil and gas extraction. Nitrous oxide emissions largely come from the microbial decomposition of fertiliser.
While methane only lasts in the atmosphere for an average of 12 years, CO2 lasts much longer. The Earth's surface absorbs CO2 as part of the carbon cycle. While plants on land and in the ocean absorb most excess emissions of CO2 every year, that CO2 is returned to the atmosphere when biological matter is digested, burns, or decays. Land-surface carbon sink processes, such as carbon fixation in the soil and photosynthesis, remove about 29% of annual global CO2 emissions. The ocean has absorbed 20 to 30% of emitted CO2 over the last 2 decades. CO2 is only removed from the atmosphere for the long term when it is stored in the Earth's crust, which is a process that can take millions of years to complete.
Land surface changes

According to Food and Agriculture Organization, around 30% of Earth's land area is largely unusable for humans (glaciers, deserts, etc.), 26% is forests, 10% is shrubland and 34% is agricultural land. Deforestation is the main land use change contributor to global warming, as the destroyed trees release CO2, and are not replaced by new trees, removing that carbon sink. Between 2001 and 2018, 27% of deforestation was from permanent clearing to enable agricultural expansion for crops and livestock. Another 24% has been lost to temporary clearing under the shifting cultivation agricultural systems. 26% was due to logging for wood and derived products, and wildfires have accounted for the remaining 23%. Some forests have not been fully cleared, but were already degraded by these impacts. Restoring these forests also recovers their potential as a carbon sink.
Local vegetation cover impacts how much of the sunlight gets reflected back into space (albedo), and how much heat is lost by evaporation. For instance, the change from a dark forest to grassland makes the surface lighter, causing it to reflect more sunlight. Deforestation can also modify the release of chemical compounds that influence clouds, and by changing wind patterns. In tropic and temperate areas the net effect is to produce significant warming, and forest restoration can make local temperatures cooler. At latitudes closer to the poles, there is a cooling effect as forest is replaced by snow-covered (and more reflective) plains. Globally, these increases in surface albedo have been the dominant direct influence on temperature from land use change. Thus, land use change to date is estimated to have a slight cooling effect.
Other factors
Aerosols and clouds
Air pollution, in the form of aerosols, affects the climate on a large scale. Aerosols scatter and absorb solar radiation. From 1961 to 1990, a gradual reduction in the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface was observed. This phenomenon is popularly known as global dimming, and is primarily attributed to sulfate aerosols produced by the combustion of fossil fuels with heavy sulfur concentrations like coal and bunker fuel. Smaller contributions come from black carbon, organic carbon from combustion of fossil fuels and biofuels, and from anthropogenic dust. Globally, aerosols have been declining since 1990 due to pollution controls, meaning that they no longer mask greenhouse gas warming as much.
Aerosols also have indirect effects on the Earth's energy budget. Sulfate aerosols act as cloud condensation nuclei and lead to clouds that have more and smaller cloud droplets. These clouds reflect solar radiation more efficiently than clouds with fewer and larger droplets. They also reduce the growth of raindrops, which makes clouds more reflective to incoming sunlight. Indirect effects of aerosols are the largest uncertainty in radiative forcing.
While aerosols typically limit global warming by reflecting sunlight, black carbon in soot that falls on snow or ice can contribute to global warming. Not only does this increase the absorption of sunlight, it also increases melting and sea-level rise. Limiting new black carbon deposits in the Arctic could reduce global warming by 0.2 °C by 2050. The effect of decreasing sulfur content of fuel oil for ships since 2020 is estimated to cause an additional 0.05 °C increase in global mean temperature by 2050.
Solar and volcanic activity

As the Sun is the Earth's primary energy source, changes in incoming sunlight directly affect the climate system. Solar irradiance has been measured directly by satellites, and indirect measurements are available from the early 1600s onwards. Since 1880, there has been no upward trend in the amount of the Sun's energy reaching the Earth, in contrast to the warming of the lower atmosphere (the troposphere). The upper atmosphere (the stratosphere) would also be warming if the Sun was sending more energy to Earth, but instead, it has been cooling. This is consistent with greenhouse gases preventing heat from leaving the Earth's atmosphere.
Explosive volcanic eruptions can release gases, dust and ash that partially block sunlight and reduce temperatures, or they can send water vapor into the atmosphere, which adds to greenhouse gases and increases temperatures. These impacts on temperature only last for several years, because both water vapor and volcanic material have low persistence in the atmosphere. volcanic CO2 emissions are more persistent, but they are equivalent to less than 1% of current human-caused CO2 emissions. Volcanic activity still represents the single largest natural impact (forcing) on temperature in the industrial era. Yet, like the other natural forcings, it has had negligible impacts on global temperature trends since the Industrial Revolution.
Climate change feedbacks

The response of the climate system to an initial forcing is modified by feedbacks: increased by "self-reinforcing" or "positive" feedbacks and reduced by "balancing" or "negative" feedbacks. The main reinforcing feedbacks are the water-vapour feedback, the ice–albedo feedback, and the net effect of clouds. The primary balancing mechanism is radiative cooling, as Earth's surface gives off more heat to space in response to rising temperature. In addition to temperature feedbacks, there are feedbacks in the carbon cycle, such as the fertilising effect of CO2 on plant growth.
Uncertainty over feedbacks, particularly cloud cover, is the major reason why different climate models project different magnitudes of warming for a given amount of emissions. As air warms, it can hold more moisture. Water vapour, as a potent greenhouse gas, holds heat in the atmosphere. If cloud cover increases, more sunlight will be reflected back into space, cooling the planet. If clouds become higher and thinner, they act as an insulator, reflecting heat from below back downwards and warming the planet.
Another major feedback is the reduction of snow cover and sea ice in the Arctic, which reduces the reflectivity of the Earth's surface. More of the Sun's energy is now absorbed in these regions, contributing to amplification of Arctic temperature changes. Arctic amplification is also thawing permafrost, which releases methane and CO2 into the atmosphere. Climate change can also cause methane releases from wetlands, marine systems, and freshwater systems. Overall, climate feedbacks are expected to become increasingly positive.
Around half of human-caused CO2 emissions have been absorbed by land plants and by the oceans. This fraction is not static and if future CO2 emissions decrease, the Earth will be able to absorb up to around 70%. If they increase substantially, it'll still absorb more carbon than now, but the overall fraction will decrease to below 40%. This is because climate change increases droughts and heat waves that eventually inhibit plant growth on land, and soils will release more carbon from dead plants when they are warmer. The rate at which oceans absorb atmospheric carbon will be lowered as they become more acidic and experience changes in thermohaline circulation and phytoplankton distribution.
Modelling

A climate model is a representation of the physical, chemical and biological processes that affect the climate system. Models include natural processes like changes in the Earth's orbit, historical changes in the Sun's activity, and volcanic forcing. Models are used to estimate the degree of warming future emissions will cause when accounting for the strength of climate feedbacks. Models also predict the circulation of the oceans, the annual cycle of the seasons, and the flows of carbon between the land surface and the atmosphere.
The physical realism of models is tested by examining their ability to simulate contemporary or past climates. Past models have underestimated the rate of Arctic shrinkage and underestimated the rate of precipitation increase. Sea level rise since 1990 was underestimated in older models, but more recent models agree well with observations. The 2017 United States-published National Climate Assessment notes that "climate models may still be underestimating or missing relevant feedback processes". Additionally, climate models may be unable to adequately predict short-term regional climatic shifts.
A subset of climate models add societal factors to a physical climate model. These models simulate how population, economic growth, and energy use affect—and interact with—the physical climate. With this information, these models can produce scenarios of future greenhouse gas emissions. This is then used as input for physical climate models and carbon cycle models to predict how atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases might change. Depending on the socioeconomic scenario and the mitigation scenario, models produce atmospheric CO2 concentrations that range widely between 380 and 1400 ppm.
Impacts

Environmental effects
The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching, affecting oceans, ice, and weather. Changes may occur gradually or rapidly. Evidence for these effects comes from studying climate change in the past, from modelling, and from modern observations. Since the 1950s, droughts and heat waves have appeared simultaneously with increasing frequency. Extremely wet or dry events within the monsoon period have increased in India and East Asia. Monsoonal precipitation over the Northern Hemisphere has increased since 1980. The rainfall rate and intensity of hurricanes and typhoons is likely increasing, and the geographic range likely expanding poleward in response to climate warming. Frequency of tropical cyclones has not increased as a result of climate change.

Global sea level is rising as a consequence of thermal expansion and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets. Between 1993 and 2020, the rise increased over time, averaging 3.3 ± 0.3 mm per year. Over the 21st century, the IPCC projects 32–62 cm of sea level rise under a low emission scenario, 44–76 cm under an intermediate one and 65–101 cm under a very high emission scenario. Marine ice sheet instability processes in Antarctica may add substantially to these values, including the possibility of a 2-meter sea level rise by 2100 under high emissions.
Climate change has led to decades of shrinking and thinning of the Arctic sea ice. While ice-free summers are expected to be rare at 1.5 °C degrees of warming, they are set to occur once every three to ten years at a warming level of 2 °C. Higher atmospheric CO2 concentrations cause more CO2 to dissolve in the oceans, which is making them more acidic. Because oxygen is less soluble in warmer water, its concentrations in the ocean are decreasing, and dead zones are expanding.
Tipping points and long-term impacts

Greater degrees of global warming increase the risk of passing through 'tipping points'—thresholds beyond which certain major impacts can no longer be avoided even if temperatures return to their previous state. For instance, the Greenland ice sheet is already melting, but if global warming reaches levels between 1.7 °C and 2.3 °C, its melting will continue until it fully disappears. If the warming is later reduced to 1.5 °C or less, it will still lose a lot more ice than if the warming was never allowed to reach the threshold in the first place. While the ice sheets would melt over millennia, other tipping points would occur faster and give societies less time to respond. The collapse of major ocean currents like the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC), and irreversible damage to key ecosystems like the Amazon rainforest and coral reefs can unfold in a matter of decades.
The long-term effects of climate change on oceans include further ice melt, ocean warming, sea level rise, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation. The timescale of long-term impacts are centuries to millennia due to CO2's long atmospheric lifetime. When net emissions stabilise surface air temperatures will also stabilise, but oceans and ice caps will continue to absorb excess heat from the atmosphere. The result is an estimated total sea level rise of 2.3 metres per degree Celsius (4.2 ft/°F) after 2000 years. Oceanic CO2 uptake is slow enough that ocean acidification will also continue for hundreds to thousands of years. Deep oceans (below 2,000 metres (6,600 ft)) are also already committed to losing over 10% of their dissolved oxygen by the warming which occurred to date. Further, West Antarctic ice sheet appears committed to practically irreversible melting, which would increase the sea levels by at least 3.3 m (10 ft 10 in) over approximately 2000 years.
Nature and wildlife
Recent warming has driven many terrestrial and freshwater species poleward and towards higher altitudes. For instance, the range of hundreds of North American birds has shifted northward at an average rate of 1.5 km/year over the past 55 years. Higher atmospheric CO2 levels and an extended growing season have resulted in global greening. However, heatwaves and drought have reduced ecosystem productivity in some regions. The future balance of these opposing effects is unclear. A related phenomenon driven by climate change is woody plant encroachment, affecting up to 500 million hectares globally. Climate change has contributed to the expansion of drier climate zones, such as the expansion of deserts in the subtropics. The size and speed of global warming is making abrupt changes in ecosystems more likely. Overall, it is expected that climate change will result in the extinction of many species.
The oceans have heated more slowly than the land, but plants and animals in the ocean have migrated towards the colder poles faster than species on land. Just as on land, heat waves in the ocean occur more frequently due to climate change, harming a wide range of organisms such as corals, kelp, and seabirds. Ocean acidification makes it harder for marine calcifying organisms such as mussels, barnacles and corals to produce shells and skeletons; and heatwaves have bleached coral reefs. Harmful algal blooms enhanced by climate change and eutrophication lower oxygen levels, disrupt food webs and cause great loss of marine life. Coastal ecosystems are under particular stress. Almost half of global wetlands have disappeared due to climate change and other human impacts.
|
Humans

The effects of climate change are impacting humans everywhere in the world. Impacts can be observed on all continents and ocean regions, with low-latitude, less developed areas facing the greatest risk. Continued warming has potentially "severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts" for people and ecosystems. The risks are unevenly distributed, but are generally greater for disadvantaged people in developing and developed countries.
Food and health
The World Health Organization (WHO) calls climate change the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century. Extreme weather leads to injury and loss of life. Various infectious diseases are more easily transmitted in a warmer climate, such as dengue fever and malaria. Crop failures can lead to food shortages and malnutrition, particularly effecting children. Both children and older people are vulnerable to extreme heat. The WHO has estimated that between 2030 and 2050, climate change would cause around 250,000 additional deaths per year. They assessed deaths from heat exposure in elderly people, increases in diarrhea, malaria, dengue, coastal flooding, and childhood malnutrition. By 2100, 50% to 75% of the global population may face climate conditions that are life-threatening due to combined effects of extreme heat and humidity.
Climate change is affecting food security. It has caused reduction in global yields of maize, wheat, and soybeans between 1981 and 2010. Future warming could further reduce global yields of major crops. Crop production will probably be negatively affected in low-latitude countries, while effects at northern latitudes may be positive or negative. Up to an additional 183 million people worldwide, particularly those with lower incomes, are at risk of hunger as a consequence of these impacts. Climate change also impacts fish populations. Globally, less will be available to be fished. Regions dependent on glacier water, regions that are already dry, and small islands have a higher risk of water stress due to climate change.
Livelihoods and inequality
Economic damages due to climate change may be severe and there is a chance of disastrous consequences. Severe impacts are expected in South-East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, where most of the local inhabitants are dependent upon natural and agricultural resources. Heat stress can prevent outdoor labourers from working. If warming reaches 4 °C then labour capacity in those regions could be reduced by 30 to 50%. The World Bank estimates that between 2016 and 2030, climate change could drive over 120 million people into extreme poverty without adaptation.
Inequalities based on wealth and social status have worsened due to climate change. Major difficulties in mitigating, adapting, and recovering to climate shocks are faced by marginalised people who have less control over resources. Indigenous people, who are subsistent on their land and ecosystems, will face endangerment to their wellness and lifestyles due to climate change. An expert elicitation concluded that the role of climate change in armed conflict has been small compared to factors such as socio-economic inequality and state capabilities.
While women are not inherently more at risk from climate change and shocks, limits on women's resources and discriminatory gender norms constrain their adaptive capacity and resilience. For example, women's work burdens, including hours worked in agriculture, tend to decline less than men's during climate shocks such as heat stress.
Climate migration
Low-lying islands and coastal communities are threatened by sea level rise, which makes urban flooding more common. Sometimes, land is permanently lost to the sea. This could lead to statelessness for people in island nations, such as the Maldives and Tuvalu. In some regions, the rise in temperature and humidity may be too severe for humans to adapt to. With worst-case climate change, models project that almost one-third of humanity might live in Sahara-like uninhabitable and extremely hot climates.
These factors can drive climate or environmental migration, within and between countries. More people are expected to be displaced because of sea level rise, extreme weather and conflict from increased competition over natural resources. Climate change may also increase vulnerability, leading to "trapped populations" who are not able to move due to a lack of resources.
|
Reducing and recapturing emissions

Climate change can be mitigated by reducing the rate at which greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere, and by increasing the rate at which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere. In order to limit global warming to less than 1.5 °C global greenhouse gas emissions needs to be net-zero by 2050, or by 2070 with a 2 °C target. This requires far-reaching, systemic changes on an unprecedented scale in energy, land, cities, transport, buildings, and industry.
The United Nations Environment Programme estimates that countries need to triple their pledges under the Paris Agreement within the next decade to limit global warming to 2 °C. An even greater level of reduction is required to meet the 1.5 °C goal. With pledges made under the Paris Agreement as of October 2021, global warming would still have a 66% chance of reaching about 2.7 °C (range: 2.2–3.2 °C) by the end of the century. Globally, limiting warming to 2 °C may result in higher economic benefits than economic costs.
Although there is no single pathway to limit global warming to 1.5 or 2 °C, most scenarios and strategies see a major increase in the use of renewable energy in combination with increased energy efficiency measures to generate the needed greenhouse gas reductions. To reduce pressures on ecosystems and enhance their carbon sequestration capabilities, changes would also be necessary in agriculture and forestry, such as preventing deforestation and restoring natural ecosystems by reforestation.
Other approaches to mitigating climate change have a higher level of risk. Scenarios that limit global warming to 1.5 °C typically project the large-scale use of carbon dioxide removal methods over the 21st century. There are concerns, though, about over-reliance on these technologies, and environmental impacts. Solar radiation modification (SRM) is also a possible supplement to deep reductions in emissions. However, SRM raises significant ethical and legal concerns, and the risks are imperfectly understood.
Clean energy
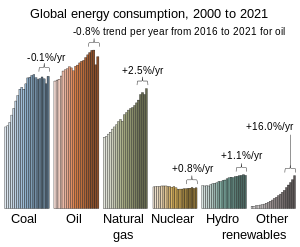

Renewable energy is key to limiting climate change. For decades, fossil fuels have accounted for roughly 80% of the world's energy use. The remaining share has been split between nuclear power and renewables (including hydropower, bioenergy, wind and solar power and geothermal energy). Fossil fuel use is expected to peak in absolute terms prior to 2030 and then to decline, with coal use experiencing the sharpest reductions. Renewables represented 75% of all new electricity generation installed in 2019, nearly all solar and wind. Other forms of clean energy, such as nuclear and hydropower, currently have a larger share of the energy supply. However, their future growth forecasts appear limited in comparison.
While solar panels and onshore wind are now among the cheapest forms of adding new power generation capacity in many locations, green energy policies are needed to achieve a rapid transition from fossil fuels to renewables. To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, renewable energy would become the dominant form of electricity generation, rising to 85% or more by 2050 in some scenarios. Investment in coal would be eliminated and coal use nearly phased out by 2050.
Electricity generated from renewable sources would also need to become the main energy source for heating and transport. Transport can switch away from internal combustion engine vehicles and towards electric vehicles, public transit, and active transport (cycling and walking). For shipping and flying, low-carbon fuels would reduce emissions. Heating could be increasingly decarbonised with technologies like heat pumps.
There are obstacles to the continued rapid growth of clean energy, including renewables. For wind and solar, there are environmental and land use concerns for new projects. Wind and solar also produce energy intermittently and with seasonal variability. Traditionally, hydro dams with reservoirs and conventional power plants have been used when variable energy production is low. Going forward, battery storage can be expanded, energy demand and supply can be matched, and long-distance transmission can smooth variability of renewable outputs. Bioenergy is often not carbon-neutral and may have negative consequences for food security. The growth of nuclear power is constrained by controversy around radioactive waste, nuclear weapon proliferation, and accidents. Hydropower growth is limited by the fact that the best sites have been developed, and new projects are confronting increased social and environmental concerns.
Low-carbon energy improves human health by minimising climate change as well as reducing air pollution deaths, which were estimated at 7 million annually in 2016. Meeting the Paris Agreement goals that limit warming to a 2 °C increase could save about a million of those lives per year by 2050, whereas limiting global warming to 1.5 °C could save millions and simultaneously increase energy security and reduce poverty. Improving air quality also has economic benefits which may be larger than mitigation costs.
Energy conservation
Reducing energy demand is another major aspect of reducing emissions. If less energy is needed, there is more flexibility for clean energy development. It also makes it easier to manage the electricity grid, and minimises carbon-intensive infrastructure development. Major increases in energy efficiency investment will be required to achieve climate goals, comparable to the level of investment in renewable energy. Several COVID-19 related changes in energy use patterns, energy efficiency investments, and funding have made forecasts for this decade more difficult and uncertain.
Strategies to reduce energy demand vary by sector. In the transport sector, passengers and freight can switch to more efficient travel modes, such as buses and trains, or use electric vehicles. Industrial strategies to reduce energy demand include improving heating systems and motors, designing less energy-intensive products, and increasing product lifetimes. In the building sector the focus is on better design of new buildings, and higher levels of energy efficiency in retrofitting. The use of technologies like heat pumps can also increase building energy efficiency.
Agriculture and industry

Agriculture and forestry face a triple challenge of limiting greenhouse gas emissions, preventing the further conversion of forests to agricultural land, and meeting increases in world food demand. A set of actions could reduce agriculture and forestry-based emissions by two thirds from 2010 levels. These include reducing growth in demand for food and other agricultural products, increasing land productivity, protecting and restoring forests, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural production.
On the demand side, a key component of reducing emissions is shifting people towards plant-based diets. Eliminating the production of livestock for meat and dairy would eliminate about 3/4ths of all emissions from agriculture and other land use. Livestock also occupy 37% of ice-free land area on Earth and consume feed from the 12% of land area used for crops, driving deforestation and land degradation.
Steel and cement production are responsible for about 13% of industrial CO2 emissions. In these industries, carbon-intensive materials such as coke and lime play an integral role in the production, so that reducing CO2 emissions requires research into alternative chemistries.
Carbon sequestration

Natural carbon sinks can be enhanced to sequester significantly larger amounts of CO2 beyond naturally occurring levels. Reforestation and afforestation (planting forests where there were none before) are among the most mature sequestration techniques, although the latter raises food security concerns. Farmers can promote sequestration of carbon in soils through practices such as use of winter cover crops, reducing the intensity and frequency of tillage, and using compost and manure as soil amendments. Forest and landscape restoration yields many benefits for the climate, including greenhouse gas emissions sequestration and reduction. Restoration/recreation of coastal wetlands, prairie plots and seagrass meadows increases the uptake of carbon into organic matter. When carbon is sequestered in soils and in organic matter such as trees, there is a risk of the carbon being re-released into the atmosphere later through changes in land use, fire, or other changes in ecosystems.
Where energy production or CO2-intensive heavy industries continue to produce waste CO2, the gas can be captured and stored instead of released to the atmosphere. Although its current use is limited in scale and expensive, carbon capture and storage (CCS) may be able to play a significant role in limiting CO2 emissions by mid-century. This technique, in combination with bioenergy (BECCS) can result in net negative emissions as CO2 is drawn from the atmosphere. It remains highly uncertain whether carbon dioxide removal techniques will be able to play a large role in limiting warming to 1.5 °C. Policy decisions that rely on carbon dioxide removal increase the risk of global warming rising beyond international goals.
Adaptation
Adaptation is "the process of adjustment to current or expected changes in climate and its effects".: 5 Without additional mitigation, adaptation cannot avert the risk of "severe, widespread and irreversible" impacts. More severe climate change requires more transformative adaptation, which can be prohibitively expensive. The capacity and potential for humans to adapt is unevenly distributed across different regions and populations, and developing countries generally have less. The first two decades of the 21st century saw an increase in adaptive capacity in most low- and middle-income countries with improved access to basic sanitation and electricity, but progress is slow. Many countries have implemented adaptation policies. However, there is a considerable gap between necessary and available finance.
Adaptation to sea level rise consists of avoiding at-risk areas, learning to live with increased flooding, and building flood controls. If that fails, managed retreat may be needed. There are economic barriers for tackling dangerous heat impact. Avoiding strenuous work or having air conditioning is not possible for everybody. In agriculture, adaptation options include a switch to more sustainable diets, diversification, erosion control, and genetic improvements for increased tolerance to a changing climate. Insurance allows for risk-sharing, but is often difficult to get for people on lower incomes. Education, migration and early warning systems can reduce climate vulnerability. Planting mangroves or encouraging other coastal vegetation can buffer storms.
Ecosystems adapt to climate change, a process that can be supported by human intervention. By increasing connectivity between ecosystems, species can migrate to more favourable climate conditions. Species can also be introduced to areas acquiring a favorable climate. Protection and restoration of natural and semi-natural areas helps build resilience, making it easier for ecosystems to adapt. Many of the actions that promote adaptation in ecosystems, also help humans adapt via ecosystem-based adaptation. For instance, restoration of natural fire regimes makes catastrophic fires less likely, and reduces human exposure. Giving rivers more space allows for more water storage in the natural system, reducing flood risk. Restored forest acts as a carbon sink, but planting trees in unsuitable regions can exacerbate climate impacts.
There are synergies but also trade-offs between adaptation and mitigation. An example for synergy is increased food productivity, which has large benefits for both adaptation and mitigation. An example of a trade-off is that increased use of air conditioning allows people to better cope with heat, but increases energy demand. Another trade-off example is that more compact urban development may reduce emissions from transport and construction, but may also increase the urban heat island effect, exposing people to heat-related health risks.
|
Policies and politics

| High | Medium | Low | Very low |
Countries that are most vulnerable to climate change have typically been responsible for a small share of global emissions. This raises questions about justice and fairness. Limiting global warming makes it much easier to achieve the UN's Sustainable Development Goals, such as eradicating poverty and reducing inequalities. The connection is recognised in Sustainable Development Goal 13 which is to "take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts". The goals on food, clean water and ecosystem protection have synergies with climate mitigation.
The geopolitics of climate change is complex. It has often been framed as a free-rider problem, in which all countries benefit from mitigation done by other countries, but individual countries would lose from switching to a low-carbon economy themselves. Sometimes mitigation also has localised benefits though. For instance, the benefits of a coal phase-out to public health and local environments exceed the costs in almost all regions. Furthermore, net importers of fossil fuels win economically from switching to clean energy, causing net exporters to face stranded assets: fossil fuels they cannot sell.
Policy options
A wide range of policies, regulations, and laws are being used to reduce emissions. As of 2019, carbon pricing covers about 20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon can be priced with carbon taxes and emissions trading systems. Direct global fossil fuel subsidies reached $319 billion in 2017, and $5.2 trillion when indirect costs such as air pollution are priced in. Ending these can cause a 28% reduction in global carbon emissions and a 46% reduction in air pollution deaths. Money saved on fossil subsidies could be used to support the transition to clean energy instead. More direct methods to reduce greenhouse gases include vehicle efficiency standards, renewable fuel standards, and air pollution regulations on heavy industry. Several countries require utilities to increase the share of renewables in power production.
Climate justice
Policy designed through the lens of climate justice tries to address human rights issues and social inequality. According to proponents of climate justice, the costs of climate adaptation should be paid by those most responsible for climate change, while the beneficiaries of payments should be those suffering impacts. One way this can be addressed in practice is to have wealthy nations pay poorer countries to adapt.
Oxfam found that in 2023 the wealthiest 10% of people were responsible for 50% of global emissions, while the bottom 50% were responsible for just 8%. Production of emissions is another way to look at responsibility: under that approach, the top 21 fossil fuel companies would owe cumulative climate reparations of $5.4 trillion over the period 2025–2050. To achieve a just transition, people working in the fossil fuel sector would also need other jobs, and their communities would need investments.
International climate agreements

Nearly all countries in the world are parties to the 1994 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The goal of the UNFCCC is to prevent dangerous human interference with the climate system. As stated in the convention, this requires that greenhouse gas concentrations are stabilised in the atmosphere at a level where ecosystems can adapt naturally to climate change, food production is not threatened, and economic development can be sustained. The UNFCCC does not itself restrict emissions but rather provides a framework for protocols that do. Global emissions have risen since the UNFCCC was signed. Its yearly conferences are the stage of global negotiations.
The 1997 Kyoto Protocol extended the UNFCCC and included legally binding commitments for most developed countries to limit their emissions. During the negotiations, the G77 (representing developing countries) pushed for a mandate requiring developed countries to "[take] the lead" in reducing their emissions, since developed countries contributed most to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Per-capita emissions were also still relatively low in developing countries and developing countries would need to emit more to meet their development needs.
The 2009 Copenhagen Accord has been widely portrayed as disappointing because of its low goals, and was rejected by poorer nations including the G77. Associated parties aimed to limit the global temperature rise to below 2 °C. The Accord set the goal of sending $100 billion per year to developing countries for mitigation and adaptation by 2020, and proposed the founding of the Green Climate Fund. As of 2020[update], only 83.3 billion were delivered. Only in 2023 the target is expected to be achieved.
In 2015 all UN countries negotiated the Paris Agreement, which aims to keep global warming well below 2.0 °C and contains an aspirational goal of keeping warming under 1.5 °C. The agreement replaced the Kyoto Protocol. Unlike Kyoto, no binding emission targets were set in the Paris Agreement. Instead, a set of procedures was made binding. Countries have to regularly set ever more ambitious goals and reevaluate these goals every five years. The Paris Agreement restated that developing countries must be financially supported. As of October 2021[update], 194 states and the European Union have signed the treaty and 191 states and the EU have ratified or acceded to the agreement.
The 1987 Montreal Protocol, an international agreement to stop emitting ozone-depleting gases, may have been more effective at curbing greenhouse gas emissions than the Kyoto Protocol specifically designed to do so. The 2016 Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol aims to reduce the emissions of hydrofluorocarbons, a group of powerful greenhouse gases which served as a replacement for banned ozone-depleting gases. This made the Montreal Protocol a stronger agreement against climate change.
National responses
In 2019, the United Kingdom parliament became the first national government to declare a climate emergency. Other countries and jurisdictions followed suit. That same year, the European Parliament declared a "climate and environmental emergency". The European Commission presented its European Green Deal with the goal of making the EU carbon-neutral by 2050. In 2021, the European Commission released its "Fit for 55" legislation package, which contains guidelines for the car industry; all new cars on the European market must be zero-emission vehicles from 2035.
Major countries in Asia have made similar pledges: South Korea and Japan have committed to become carbon-neutral by 2050, and China by 2060. While India has strong incentives for renewables, it also plans a significant expansion of coal in the country. Vietnam is among very few coal-dependent, fast-developing countries that pledged to phase out unabated coal power by the 2040s or as soon as possible thereafter.
As of 2021, based on information from 48 national climate plans, which represent 40% of the parties to the Paris Agreement, estimated total greenhouse gas emissions will be 0.5% lower compared to 2010 levels, below the 45% or 25% reduction goals to limit global warming to 1.5 °C or 2 °C, respectively.
Society
Denial and misinformation
Public debate about climate change has been strongly affected by climate change denial and misinformation, which originated in the United States and has since spread to other countries, particularly Canada and Australia. Climate change denial has originated from fossil fuel companies, industry groups, conservative think tanks, and contrarian scientists. Like the tobacco industry, the main strategy of these groups has been to manufacture doubt about climate-change related scientific data and results. People who hold unwarranted doubt about climate change are called climate change "skeptics", although "contrarians" or "deniers" are more appropriate terms.
There are different variants of climate denial: some deny that warming takes place at all, some acknowledge warming but attribute it to natural influences, and some minimise the negative impacts of climate change. Manufacturing uncertainty about the science later developed into a manufactured controversy: creating the belief that there is significant uncertainty about climate change within the scientific community in order to delay policy changes. Strategies to promote these ideas include criticism of scientific institutions, and questioning the motives of individual scientists. An echo chamber of climate-denying blogs and media has further fomented misunderstanding of climate change.
Public awareness and opinion

Climate change came to international public attention in the late 1980s. Due to media coverage in the early 1990s, people often confused climate change with other environmental issues like ozone depletion. In popular culture, the climate fiction movie The Day After Tomorrow (2004) and the Al Gore documentary An Inconvenient Truth (2006) focused on climate change.
Significant regional, gender, age and political differences exist in both public concern for, and understanding of, climate change. More highly educated people, and in some countries, women and younger people, were more likely to see climate change as a serious threat. Partisan gaps also exist in many countries, and countries with high CO2 emissions tend to be less concerned. Views on causes of climate change vary widely between countries. Concern has increased over time, to the point where in 2021 a majority of citizens in many countries express a high level of worry about climate change, or view it as a global emergency. Higher levels of worry are associated with stronger public support for policies that address climate change.
Climate movement
Climate protests demand that political leaders take action to prevent climate change. They can take the form of public demonstrations, fossil fuel divestment, lawsuits and other activities. Prominent demonstrations include the School Strike for Climate. In this initiative, young people across the globe have been protesting since 2018 by skipping school on Fridays, inspired by Swedish teenager Greta Thunberg. Mass civil disobedience actions by groups like Extinction Rebellion have protested by disrupting roads and public transport.
Litigation is increasingly used as a tool to strengthen climate action from public institutions and companies. Activists also initiate lawsuits which target governments and demand that they take ambitious action or enforce existing laws on climate change. Lawsuits against fossil-fuel companies generally seek compensation for loss and damage.
History
Early discoveries

Scientists in the 19th century such as Alexander von Humboldt began to foresee the effects of climate change. In the 1820s, Joseph Fourier proposed the greenhouse effect to explain why Earth's temperature was higher than the Sun's energy alone could explain. Earth's atmosphere is transparent to sunlight, so sunlight reaches the surface where it is converted to heat. However, the atmosphere is not transparent to heat radiating from the surface, and captures some of that heat, which in turn warms the planet.
In 1856 Eunice Newton Foote demonstrated that the warming effect of the Sun is greater for air with water vapour than for dry air, and that the effect is even greater with carbon dioxide (CO2). She concluded that "An atmosphere of that gas would give to our earth a high temperature..."

Starting in 1859, John Tyndall established that nitrogen and oxygen—together totaling 99% of dry air—are transparent to radiated heat. However, water vapour and gases such as methane and carbon dioxide absorb radiated heat and re-radiate that heat into the atmosphere. Tyndall proposed that changes in the concentrations of these gases may have caused climatic changes in the past, including ice ages.
Svante Arrhenius noted that water vapour in air continuously varied, but the CO2 concentration in air was influenced by long-term geological processes. Warming from increased CO2 levels would increase the amount of water vapour, amplifying warming in a positive feedback loop. In 1896, he published the first climate model of its kind, projecting that halving CO2 levels could have produced a drop in temperature initiating an ice age. Arrhenius calculated the temperature increase expected from doubling CO2 to be around 5–6 °C. Other scientists were initially skeptical and believed that the greenhouse effect was saturated so that adding more CO2 would make no difference, and that the climate would be self-regulating. Beginning in 1938, Guy Stewart Callendar published evidence that climate was warming and CO2 levels were rising, but his calculations met the same objections.
Development of a scientific consensus

In the 1950s, Gilbert Plass created a detailed computer model that included different atmospheric layers and the infrared spectrum. This model predicted that increasing CO2 levels would cause warming. Around the same time, Hans Suess found evidence that CO2 levels had been rising, and Roger Revelle showed that the oceans would not absorb the increase. The two scientists subsequently helped Charles Keeling to begin a record of continued increase, which has been termed the "Keeling Curve". Scientists alerted the public, and the dangers were highlighted at James Hansen's 1988 Congressional testimony. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), set up in 1988 to provide formal advice to the world's governments, spurred interdisciplinary research. As part of the IPCC reports, scientists assess the scientific discussion that takes place in peer-reviewed journal articles.
There is a near-complete scientific consensus that the climate is warming and that this is caused by human activities. As of 2019, agreement in recent literature reached over 99%. No scientific body of national or international standing disagrees with this view. Consensus has further developed that some form of action should be taken to protect people against the impacts of climate change. National science academies have called on world leaders to cut global emissions. The 2021 IPCC Assessment Report stated that it is "unequivocal" that climate change is caused by humans.
See also
- Anthropocene – proposed geological time interval in which humans are having significant geological impact
- List of climate scientists
References
Other peer-reviewed sources
Books, reports and legal documents
Non-technical sources
External links
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Climate change, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.


![A dry lakebed in California, which is experiencing its worst megadrought in 1,200 years.[17]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d3/California_Drought_Dry_Lakebed_2009.jpg/129px-California_Drought_Dry_Lakebed_2009.jpg)