Global Surface Temperature
Global surface temperature (GST) refers to the average temperature of Earth's surface.
It is determined nowadays by measuring the temperatures over the ocean and land, and then calculating a weighted average. The temperature over the ocean is called the sea surface temperature. The temperature over land is called the surface air temperature. Temperature data comes mainly from weather stations and satellites. To estimate data in the distant past, proxy data can be used for example from tree rings, corals, and ice cores. Observing the rising GST over time is one of the many lines of evidence supporting the scientific consensus on climate change, which is that human activities are causing climate change.

Alternative terms for the same thing are global mean surface temperature (GMST) or global average surface temperature.
Series of reliable global temperature measurements began in the 1850—1880 time frame (this is called the instrumental temperature record). Through 1940, the average annual temperature increased, but was relatively stable between 1940 and 1975. Since 1975, it has increased by roughly 0.15 °C to 0.20 °C per decade, to at least 1.1 °C (1.9 °F) above 1880 levels. The current annual GMST is about 15 °C (59 °F), though monthly temperatures can vary almost 2 °C (4 °F) above or below this figure.
Definition
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines global mean surface temperature (GMST) as follows: GMST is the "estimated global average of near-surface air temperatures over land and sea ice, and sea surface temperature (SST) over ice-free ocean regions, with changes normally expressed as departures from a value over a specified reference period".: 2231
In comparison, the global mean surface air temperature (GSAT) is the "global average of near-surface air temperatures over land, oceans and sea ice. Changes in GSAT are often used as a measure of global temperature change in climate models.": 2231
Relevance
Changes in global temperatures over the past century provide evidence for the effects of increasing greenhouse gasses. When the climate system reacts to such changes, climate change follows. Measurement of the GST(global surface temperature) is one of the many lines of evidence supporting the scientific consensus on climate change, which is that humans are causing warming of Earth's climate system.

Measurement and calculation
The global surface temperature (GST) is calculated by averaging the temperatures over sea (sea surface temperature) and land (surface air temperature).
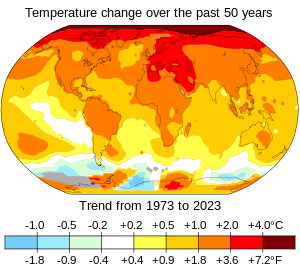
Instrumental temperature records are based on direct, instrument-based measurements of air temperature and ocean temperature, unlike indirect reconstructions using climate proxy data such as from tree rings and ocean sediments. The longest-running temperature record is the Central England temperature data series, which starts in 1659. The longest-running quasi-global records start in 1850. Temperatures on other time scales are explained in global temperature record.
"Global temperature" can have different definitions. There is a small difference between air and surface temperatures.: 12Observations

Global warming affects all parts of Earth's climate system. Global surface temperatures have risen by 1.1 °C (2.0 °F). Scientists say they will rise further in the future. The changes in climate are not uniform across the Earth. In particular, most land areas have warmed faster than most ocean areas. The Arctic is warming faster than most other regions. Night-time temperatures have increased faster than daytime temperatures. The impact on nature and people depends on how much more the Earth warms.: 787
Scientists use several methods to predict the effects of human-caused climate change. One is to investigate past natural changes in climate. To assess changes in Earth's past climate scientists have studied tree rings, ice cores, corals, and ocean and lake sediments. These show that recent temperatures have surpassed anything in the last 2,000 years. By the end of the 21st century, temperatures may increase to a level last seen in the mid-Pliocene. This was around 3 million years ago.: 322 At that time, mean global temperatures were about 2–4 °C (3.6–7.2 °F) warmer than pre-industrial temperatures. The global mean sea level was up to 25 metres (82 ft) higher than it is today.: 323 The modern observed rise in temperature and CO2 concentrations has been rapid. even abrupt geophysical events in Earth's history do not approach current rates.: 54Effects
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an overall warming trend, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather. As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification. These changes can profoundly impact ecosystems and societies, and can become irreversible once tipping points are crossed.
The effects of climate change vary in timing and location. Up until now the Arctic has warmed faster than most other regions due to climate change feedbacks. Surface air temperatures over land have also increased at about twice the rate they do over the ocean, causing intense heat waves. These temperatures would stabilize if greenhouse gas emissions were brought under control. Ice sheets and oceans absorb the vast majority of excess heat in the atmosphere, delaying effects there but causing them to accelerate and then continue after surface temperatures stabilize. Sea level rise is a particular long term concern as a result. The effects of ocean warming also include deoxygenation from marine heatwaves, ocean stratification, and changes to ocean currents.: 10 The ocean is also acidifying as it absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

See also
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Global surface temperature, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.



