貴
| ||||||||
Translingual edit
Han character edit
貴 (Kangxi radical 154, 貝+5, 12 strokes, cangjie input 中一月山金 (LMBUC), four-corner 50806, composition ⿱𠀐貝)
Derived characters edit
- 僓, 𭂟, 嘳, 墤, 嬇, 𭘵, 憒, 撌, 潰, 𤡱, 隤, 𣄜, 𭧫, 樻, 殨, 𤏳, 𤗴, 璝, 膭, 𥀠, 瞶, 𥢢, 䙡, 𥼩, 繢, 聵, 𦪒, 𧑋, 𧗏, 䜋, 𧲆, 𧸃, 蹪, 䠿, 𨎨, 𨣈, 鐀, 靧, 鞼, 𩏡, 饋, 𩡞, 𬳱, 䯣, 𫙷
- 尵, 遺, 𫵒, 𠒺, 𩘺, 𧸯, 𭅁, 䫭, 𬐲, 𡪲, 蕢, 𧷅, 簣, 䰎, 𢊮, 㿉, 𨲿, 𪎯, 闠, 𮤩, 匱, 圚, 𧷩, 𨆨
Descendants edit
References edit
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 1206, character 15
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 36704
- Dae Jaweon: page 1669, character 5
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 6, page 3632, character 9
- Unihan data for U+8CB4
Chinese edit
| trad. | 貴 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 贵 | |
| alternative forms | 䝿 𧷈 𧸋 𡭙 | |
Glyph origin edit
| Historical forms of the character 貴 | |
|---|---|
| Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
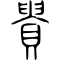 |  |
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 藬 | *l'uːl |
| 僓 | *l̥ʰuːlʔ, *ɡluːds |
| 頹 | *l'uːl |
| 穨 | *l'uːl |
| 蘈 | *l'uːl |
| 隤 | *l'uːl |
| 墤 | *l'uːl, *kʰruːds |
| 尵 | *l'uːl, *r'uːl |
| 蹪 | *l'uːl |
| 瀢 | *l'uːlʔ, *lulʔ |
| 鞼 | *kluːl, *ɡruls |
| 膭 | *kluːl, *ɡluːls |
| 憒 | *kluːds |
| 靧 | *ɡluːds |
| 潰 | *ɡluːls |
| 繢 | *ɡluːds |
| 嬇 | *ɡluːds, *kʰruːds |
| 殨 | *ɡluːds |
| 闠 | *ɡluːds |
| 簣 | *kʰruːds, *ɡruds |
| 嘳 | *kʰruːds, *kʰruds |
| 蕢 | *kʰruːds, *ɡruds |
| 聵 | *ŋɡruːds |
| 樻 | *kʰruds, *ɡruds |
| 䙡 | *kʰruds, *kʰluds |
| 匱 | *ɡruds |
| 臾 | *ɡruds, *lo |
| 饋 | *ɡruls |
| 櫃 | *ɡruds |
| 遺 | *lul, *luls |
| 壝 | *lul, *lulʔ |
| 瞶 | *luls, *kluls |
| 貴 | *kluds |
Simplified from 䝿 (臾 → 𠀐). Phono-semantic compound (形聲/形声, OC *kluds) : phonetic 臾 (OC *ɡruds, *lo) + semantic 貝 (“money cowrie”).
Etymology edit
From Sino-Tibetan; compare Tibetan གུས (gus, “respect, reverence, devotion”) (Schuessler, 2007; STEDT).
Pronunciation edit
Definitions edit
貴
- expensive; costly
- precious; valuable
- superior; noble
- 富與貴是人之所欲也,不以其道得之,不處也;貧與賤是人之所惡也,不以其道得之,不去也。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Analects of Confucius, c. 475 – 221 BCE, translated based on James Legge's version
- Fù yǔ guì shì rén zhī suǒ yù yě, bù yǐ qí dào dé zhī, bù chù yě; pín yǔ jiàn shì rén zhī suǒ è yě, bù yǐ qí dào dé zhī, bù qù yě. [Pinyin]
- Riches and honors are what men desire. If it cannot be obtained in the proper way, they should not be held. Poverty and meanness are what men dislike. If it cannot be avoided in the proper way, they should not be avoided.
富与贵是人之所欲也,不以其道得之,不处也;贫与贱是人之所恶也,不以其道得之,不去也。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- to regard as valuable
- (humble) your (to a deity, person or establishment)
- Short for 貴州/贵州 (Guìzhōu).
- a surname
Synonyms edit
| Variety | Location | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Classical Chinese | 貴 | |
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 貴, 昂貴, 高昂 | |
| Mandarin | Beijing | 貴 |
| Taiwan | 貴 | |
| Jinan | 貴 | |
| Xi'an | 貴 | |
| Wuhan | 貴 | |
| Chengdu | 貴 | |
| Guilin | 貴 | |
| Yangzhou | 貴 | |
| Hefei | 貴 | |
| Malaysia | 貴 | |
| Singapore | 貴 | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | 貴 |
| Hong Kong | 貴 | |
| Hong Kong (San Tin Weitou) | 貴 | |
| Hong Kong (Ting Kok) | 貴 | |
| Hong Kong (Tung Ping Chau) | 貴 | |
| Yangjiang | 貴 | |
| Singapore (Guangfu) | 貴 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 貴 |
| Hakka | Meixian | 貴 |
| Miaoli (N. Sixian) | 貴 | |
| Pingtung (Neipu; S. Sixian) | 貴 | |
| Hsinchu County (Zhudong; Hailu) | 貴 | |
| Taichung (Dongshi; Dabu) | 貴 | |
| Hsinchu County (Qionglin; Raoping) | 貴 | |
| Yunlin (Lunbei; Zhao'an) | 貴 | |
| Hong Kong | 貴 | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 貴 |
| Northern Min | Jian'ou | 貴 |
| Eastern Min | Fuzhou | 貴 |
| Southern Min | Xiamen | 貴 |
| Singapore (Hokkien) | 貴 | |
| Manila (Hokkien) | 貴 | |
| Chaozhou | 貴 | |
| Zhongshan Min | Shaxi (Longdu) | 貴 |
| Wu | Suzhou | 貴 |
| Wenzhou | 貴 | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 貴 |
| Shuangfeng | 貴 | |
Usage notes edit
In Hong Kong and Taiwan, a space is often left before this word when it is used as a humble term of "your" to show respect when writing formal letters, and this practice is known as 抬頭/抬头 (táitóu). This practice, however, is not common in Mainland China.
Compounds edit
- 中貴人/中贵人
- 人貴自知/人贵自知 (rén guì zìzhī)
- 兵貴神速/兵贵神速 (bīngguìshénsù)
- 功名富貴/功名富贵 (gōngmíng fùguì)
- 勛貴/勋贵
- 可貴/可贵 (kěguì)
- 名貴/名贵 (míngguì)
- 單身貴族/单身贵族 (dānshēn guìzú)
- 坐富貴/坐富贵
- 坐床富貴/坐床富贵
- 多賤寡貴/多贱寡贵
- 大官富貴/大官富贵
- 大富大貴/大富大贵
- 夫榮妻貴/夫荣妻贵
- 天潢貴胄/天潢贵胄
- 天貴/天贵
- 夫貴妻榮/夫贵妻荣
- 天貴星/天贵星
- 妻以夫貴/妻以夫贵
- 嬌貴/娇贵 (jiāoguì)
- 富貴/富贵 (fùguì)
- 富貴不淫/富贵不淫
- 富貴人家/富贵人家
- 富貴利達/富贵利达
- 富貴功名/富贵功名
- 富貴在天/富贵在天
- 富貴壽考/富贵寿考
- 富貴有餘/富贵有余
- 富貴榮華/富贵荣华
- 富貴浮雲/富贵浮云
- 富貴無常/富贵无常
- 富貴花/富贵花
- 富貴花開/富贵花开
- 富貴衣/富贵衣
- 富貴豪宕/富贵豪宕
- 富貴逼人/富贵逼人
- 富貴風流/富贵风流
- 富貴驕人/富贵骄人
- 寵貴/宠贵
- 寶貴/宝贵 (bǎoguì)
- 尊師貴道/尊师贵道
- 尊貴/尊贵 (zūnguì)
- 屨賤踊貴/屦贱踊贵
- 彌足珍貴/弥足珍贵 (mízúzhēnguì)
- 挾貴/挟贵
- 挾貴倚勢/挟贵倚势
- 接貴攀高/接贵攀高
- 攀高接貴/攀高接贵
- 攀高結貴/攀高结贵
- 文貴天成/文贵天成
- 新貴/新贵 (xīnguì)
- 早生貴子/早生贵子 (zǎoshēngguìzǐ)
- 昂貴/昂贵 (ángguì)
- 暴貴/暴贵
- 朝貴/朝贵 (cháoguì)
- 朱一貴/朱一贵
- 柴荒米貴/柴荒米贵
- 楊貴妃/杨贵妃 (Yáng Guìfēi)
- 楊貴店/杨贵店 (Yángguìdiàn)
- 榮華富貴/荣华富贵 (rónghuáfùguì)
- 權貴/权贵 (quánguì)
- 權貴顯要/权贵显要
- 母以子貴/母以子贵 (mǔyǐzǐguì)
- 洛陽紙貴/洛阳纸贵 (luòyángzhǐguì)
- 浮雲富貴/浮云富贵
- 清貴/清贵
- 物離鄉貴/物离乡贵
- 王公貴人/王公贵人
- 王公貴戚/王公贵戚
- 珍貴/珍贵 (zhēnguì)
- 發富發貴/发富发贵
- 矜貴/矜贵 (jīnguì)
- 窮富極貴/穷富极贵
- 窮貴極富/穷贵极富
- 紆尊降貴/纡尊降贵 (yūzūnjiàngguì)
- 細貴/细贵
- 翔貴/翔贵
- 至尊至貴/至尊至贵
- 良貴/良贵
- 華貴/华贵 (huáguì)
- 親貴/亲贵
- 誅不避貴/诛不避贵
- 論貴粟疏/论贵粟疏
- 豪門貴胄/豪门贵胄
- 貴上/贵上
- 貴不凌賤/贵不凌贱
- 貴不可言/贵不可言 (guì bùkě yán)
- 貴主/贵主
- 貴人/贵人 (guìrén)
- 貴人多忘/贵人多忘
- 貴介/贵介
- 貴仕/贵仕
- 貴价
- 貴勢炎炎/贵势炎炎
- 貴古賤今/贵古贱今
- 貴品/贵品
- 貴國/贵国 (guìguó)
- 貴地/贵地
- 貴女/贵女
- 貴妃/贵妃 (guìfēi)
- 貴妃醉酒/贵妃醉酒
- 貴姓/贵姓 (guìxìng)
- 貴婦/贵妇 (guìfù)
- 貴婿/贵婿
- 貴嬪/贵嫔
- 貴官/贵官
- 貴客/贵客 (guìkè)
- 貴寓/贵寓
- 貴寵/贵宠
- 貴嶼/贵屿 (Guìyǔ)
- 貴州/贵州 (Guìzhōu)
- 貴幸/贵幸
- 貴幹/贵干 (guìgàn)
- 貴府/贵府
- 貴庚/贵庚 (guìgēng)
- 貴徵/贵征
- 貴德/贵德 (guìdé)
- 貴志/贵志
- 貴恙/贵恙 (guìyàng)
- 貴戚/贵戚 (guìqī)
- 貴方/贵方 (guìfāng)
- 貴族/贵族 (guìzú)
- 貴族子弟/贵族子弟
- 貴族學校/贵族学校
- 貴族政治/贵族政治 (guìzú zhèngzhì)
- 貴族文學/贵族文学
- 貴族院/贵族院 (Guìzúyuàn)
- 貴會/贵会
- 貴極人臣/贵极人臣
- 貴無常尊/贵无常尊
- 貴甲子/贵甲子
- 貴男/贵男
- 貴相/贵相
- 貴社/贵社 (guìshè)
- 貴細/贵细
- 貴耳賤目/贵耳贱目
- 貴胄/贵胄
- 貴處/贵处
- 貴要/贵要
- 貴貴/贵贵
- 貴賓/贵宾 (guìbīn)
- 貴賓卡/贵宾卡
- 貴賤/贵贱 (guìjiàn)
- 貴賤之別/贵贱之别
- 貴賤無二/贵贱无二
- 貴賤無常/贵贱无常
- 貴賤高下/贵贱高下
- 貴近/贵近
- 貴造/贵造
- 貴遊子弟/贵游子弟
- 貴遠賤近/贵远贱近
- 貴遠鄙近/贵远鄙近
- 貴重/贵重 (guìzhòng)
- 貴金屬/贵金属 (guìjīnshǔ)
- 貴降/贵降
- 貴陽/贵阳 (Guìyáng)
- 貴陽市/贵阳市
- 貴霜王朝/贵霜王朝
- 貴顯/贵显 (guìxiǎn)
- 貴體/贵体 (guìtǐ)
- 貴體違和/贵体违和
- 賤斂貴出/贱敛贵出
- 賤斂貴發/贱敛贵发
- 賤貴窮通/贱贵穷通
- 賤買貴賣/贱买贵卖
- 踊貴
- 踊貴屨賤/踊贵屦贱
- 踴貴/踊贵
- 輕財貴義/轻财贵义
- 達官貴人/达官贵人 (dáguānguìrén)
- 長命富貴/长命富贵
- 阿尊事貴/阿尊事贵
- 降貴紆尊/降贵纡尊
- 隆貴/隆贵
- 雍容華貴/雍容华贵
- 難能可貴/难能可贵 (nánnéngkěguì)
- 雲貴川/云贵川 (Yúnguìchuān)
- 雲貴高原/云贵高原 (Yún-Guì Gāoyuán)
- 顯貴/显贵 (xiǎnguì)
- 騰貴/腾贵 (téngguì)
- 驕貴/骄贵
- 體貴心驕/体贵心骄
- 高抬貴手/高抬贵手 (gāotáiguìshǒu)
- 高貴/高贵 (gāoguì)
- 高貴不貴/高贵不贵
- 高貴優雅/高贵优雅
- 鼠憑社貴/鼠凭社贵
References edit
- “貴”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[1], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
- “Entry #9061”, in 臺灣閩南語常用詞辭典 (overall work in Mandarin and Hokkien), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2023.
Japanese edit
Kanji edit
- expensive (たかい)
- worthful, precious (たかい, とうとい, たっとい)
- superior, aristocratic (たかい, とうとい, たっとい, えらい, あてやか)
- to esteem (とうとぶ, たっとぶ)
Readings edit
- Go-on: き (ki, Jōyō)←き (ki, historical)←くゐ (kwi, ancient)
- Kan-on: き (ki, Jōyō)←き (ki, historical)←くゐ (kwi, ancient)
- Kun: たかい (takai, 貴い); たっとい (tattoi, 貴い, Jōyō)←たつとい (tatutoi, 貴い, historical); とうとい (tōtoi, 貴い, Jōyō)←たふとい (tafutoi, 貴い, historical); たっとぶ (tattobu, 貴ぶ, Jōyō)←たつとぶ (tatutobu, 貴ぶ, historical); とうとぶ (tōtobu, 貴ぶ, Jōyō)←たふとぶ (tafutobu, 貴ぶ, historical)
- Nanori: きよ (kiyo); ぎ (gi); たか (taka); たかし (takashi); よし (yoshi)
Compounds edit
Etymology 1 edit
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 貴 |
| き Grade: 6 |
| goon |
From Middle Chinese 貴 (MC kjw+jH, literally “precious, noble, superior”).
Pronunciation edit
Prefix edit
- (archaic) added to nouns related to people to indicate superiority
- 貴公子、貴婦人、貴賓
- kikōshi, kifujin, kihin
- [young] nobleman, noblewoman, superior guest
- 貴公子、貴婦人、貴賓
- (archaic) added to nouns to indicate respect and possession: your
- 貴店
- kiten
- your [honorable] store
- 貴店
Derived terms edit
Suffix edit
- added after nouns related to people to express love and respect
Usage notes edit
This suffix meaning appears from roughly the Edo period.
Derived terms edit
Etymology 2 edit
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 貴 |
| あて Grade: 6 |
| kun’yomi |
Unknown. Possibly cognate with 当て (ate, “aim; expectation, hope”), the 連用形 (ren'yōkei, “stem or continuative form”) of the verb 当てる (ateru, “to face one thing towards another; to make something hit a target”).
Pronunciation edit
Adjective edit
Inflection edit
| Stem forms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrealis (未然形) | 貴なら | あてなら | atenara | |
| Continuative (連用形) | 貴に[1] 貴なり[2] | あてに あてなり | ateni atenari | |
| Terminal (終止形) | 貴なり | あてなり | atenari | |
| Attributive (連体形) | 貴なる | あてなる | atenaru | |
| Realis (已然形) | 貴なれ | あてなれ | atenare | |
| Imperative (命令形) | 貴なれ | あてなれ | atenare | |
| Key constructions | ||||
| Negative | 貴ならず | あてならず | atenarazu | |
| Contrasting conjunction | 貴なれど | あてなれど | atenaredo | |
| Causal conjunction | 貴なれば | あてなれば | atenareba | |
| Conditional conjunction | 貴ならば | あてならば | atenaraba | |
| Past tense (firsthand knowledge) | 貴なりき | あてなりき | atenariki | |
| Past tense (secondhand knowledge) | 貴なりけり | あてなりけり | atenarikeri | |
| Adverbial | 貴に | あてに | ateni | |
| [1]Without auxiliary verb. [2]With auxiliary verb. | ||||
Noun edit
- (archaic) one's own father (by extension of the “noble” meaning)
- 1028-1107: 栄花物語 (Eiga Monogatari, “Tale of Splendor”)
- 貴は麿をば恋しとは思ひ給はぬか
- Ate wa maro oba koishi to wa omohitamahanu ka
- Doesn't father think I'm his darling?
- 貴は麿をば恋しとは思ひ給はぬか
- 1028-1107: 栄花物語 (Eiga Monogatari, “Tale of Splendor”)
Derived terms edit
Etymology 3 edit
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 貴 |
| むち Grade: 6 |
| kun’yomi |
Possibly a compound of 身 (mu, “body”) + 霊 (chi, “spirit, essence, soul”).[1] Alternatively, may be an alteration of 睦 (mutsu, “friendly, harmonious”, affix not used in isolation),[1] in a manner similar to the alteration between kamu (combining form) and kami (standalone form) for 神 (“god, spirit”), or kutsu (combining form) and kuchi (standalone form) for 口 (“mouth”).
Pronunciation edit
Noun edit
Derived terms edit
Etymology 4 edit
Used as ateji in various names.
Proper noun edit
貴 • (Ateshi)
- a male given name
Proper noun edit
- a male given name
- a surname
Proper noun edit
- a male given name
Proper noun edit
- a male given name
Proper noun edit
- a male given name
Proper noun edit
貴 • (Kisaki)
- a surname
References edit
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shōgaku Tosho (1988) 国語大辞典(新装版) [Unabridged Dictionary of Japanese (Revised Edition)] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN
Korean edit
Hanja edit
Vietnamese edit
Han character edit
貴: Hán Nôm readings: quý, quí, quới
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.