Milky Way
The Milky Way is our home galaxy.
It contains around 400 billion stars, including our Sun.
| Milky Way | |
|---|---|
 The Milky Way's galactic center in the night sky above the Paranal Observatory (the laser creates a guide for the telescope) | |
| Observation data | |
| Distance | 26.4 ± 1.0 kly (8.09 ± 0.31 kpc) (from Sun) |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | Sb, Sbc, or SB(rs)bc (barred spiral galaxy) |
| Mass | 0.8–1.5×1012 M☉ M☉ |
| Number of stars | 100–400 billion [(1–4)×1011] |
The Milky Way has a diameter of 26.8 ± 1.1 kiloparsecs (87,400 ± 3,600 light-years) as measured using the D25isophote, and is a barred spiral galaxy. The idea that the Milky Way is made of stars goes back to the Ancient Greek philosopher Democritus.
The Milky Way has three main parts: a disk, where the Solar System is, a bulge at the core, and an outer halo all around it. Although the word "disk" suggests it is flat, the Milky Way is actually not quite flat. It is slightly warped and twisted.
This galaxy belongs to the Local Group of three large galaxies and over 50 smaller galaxies. The Milky Way is one of the largest galaxies in the group, second to the Andromeda Galaxy. Its closest neighbour is the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy, which is about 25,000 light years away from the Earth. The Andromeda Galaxy is moving towards the Milky Way Galaxy and will collide with it in about 3.75 billion years. The Andromeda Galaxy moves with a speed of about 1,800 kilometres per minute.
Origin: "Two of the Milky Way's earliest building blocks" are known; Shakti and Shiva seem "to be (left-overs or) remnants of two galaxies that (were joined or) merged ... with an early version of the Milky Way"; That seems to have happened "between 12 and 13 billion years ago";.
Size
The stellar disk of the Milky Way Galaxy is about 200,000 light-years (9×1017 km) in diameter, and is considered to be, on average, about 1000 light years thick.
It is estimated to contain at least 100 billion stars, and possibly up to 400 billion stars. The figure depends on the number of very low-mass, or dwarf stars, which are hard to detect, especially more than 300 light years from our sun. Therefore, present estimates of the total number are uncertain. This can be compared to the one trillion (1012) stars of the neighbouring Andromeda Galaxy.
The stellar disc of the Milky Way does not have a sharp edge, a radius beyond which there are no stars. Rather, the number of stars drops smoothly with distance from the centre of the Galaxy. Beyond a radius of about 40,000 light years, the number of stars drops much faster, for reasons that are not understood.
Extending beyond the stellar disk is a much thicker disk of gas. Observations indicate that the gaseous disk of the Milky Way has a thickness of around 12000 light years–twice the previously accepted value.
At 220 kilometers per second it takes the Solar System about 240 million years to complete one orbit of the Galaxy (a galactic year).
The Galactic halo extends outward but is limited in size by the orbits of two Milky Way satellites, the Large and the Small Magellanic Clouds, whose closest approach is at about 180,000 light years. At this distance or beyond, the orbits of most halo objects would be disrupted by the Magellanic Clouds, and the objects would likely be ejected from the vicinity of the Milky Way.
As a guide to the relative physical scale of the Milky Way, if the Solar System out to the orbit of Pluto were reduced to the size of a US quarter (about an inch or 25 mm in diameter), the Milky Way would have a diameter of 2,000 kilometers.
Galactic center
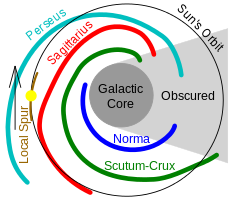

The galactic disc, which bulges outward at the galactic center, has a diameter of 170–200,000 light years.
The exact distance from the Sun to the galactic center is debated. The latest estimates give distances to the Galactic center of 25–28,000 light years.
The movement of material around the galactic center shows that it has a compact object of very large mass. The intense radio source named Sagittarius A*, thought to mark the center of the Milky Way, is now confirmed to be a supermassive black hole. Most galaxies are believed to have a supermassive black hole at their center.
Most galaxies have a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. The nature of the Milky Way's bar is actively debated, with estimates for its half-length and orientation spanning from 3,300 to 16,000 light years (short or a long bar) and 10–50 degrees. Viewed from the Andromeda Galaxy, it would be the brightest feature of our own galaxy.
Mythology
In Greek mythology, Zeus places his son (the baby Heracles) whose mother was a mortal woman on Hera's breast while she is sleeping so that the baby will drink her divine milk and become immortal. However, Hera wakes up while she is breastfeeding the baby and realizes she is nursing a baby she does not know. According to Greek mythology, she then pushes the baby away and a stream of her milk sprays the night sky, making a faint band of light known as the Milky Way.
References
Related pages

This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Milky Way, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.