Mathematics Matrix: Rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns
In mathematics, a matrix (plural: matrices) is a rectangle of numbers, arranged in rows and columns.
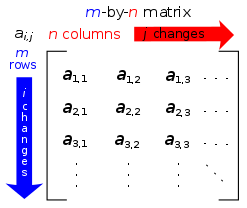
The rows are each left-to-right (horizontal) lines, and the columns go top-to-bottom (vertical). The top-left cell is at row 1, column 1 (see diagram at right).
Matrices are often represented by capital roman letters such as , and , and there are rules for adding, subtracting and "multiplying" matrices together, but the rules are different than for numbers. As an example, the product does not always give the same result as , which is the case for the multiplication of ordinary numbers. A matrix can have more than 2 dimensions, such as a 3D matrix. Also, a matrix can be one-dimensional, as a single row or a single column.
Many natural sciences use matrices quite a lot. In many universities, courses about matrices (usually called linear algebra) are taught very early, sometimes even in the first year of studies. Matrices are also very common in computer science, engineering, physics, economics, and statistics.
Definitions and notations
The horizontal lines in a matrix are called rows. The vertical lines are called columns. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m-by-n matrix (or m×n matrix). m and n are called its dimensions.
The places in the matrix where the numbers are, are called entries. The entry of a matrix called "A" that is in the row number i and column number j is called the i,j entry of A. This is written as A[i,j] or ai,j.

Example
The matrix
is a 4×3 matrix. This matrix has m=4 rows, and n=3 columns.
The element A[2,3] or a2,3 is 7.
Operations
Addition
The sum of two matrices is the matrix, which (i,j)-th entry is equal to the sum of the (i,j)-th entries of two matrices:
The two matrices have the same dimensions. Here, 
Multiplication of two matrices
The multiplication of two matrices is a bit more complicated:
This is an example with numbers:
- Sometimes, two matrices can be multiplied with each other even if they have different dimensions. For this, the number of columns in the first matrix has to be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix.
- The result of the multiplication is called the product. The product is another matrix. It has the same number of rows as the first matrix and the same number of columns as the second matrix.
- The multiplication of matrices is not commutative, which means that in general,
.
- The multiplication of matrices is associative, which means that
.
Special matrices
There are some matrices that are special.
Square matrix
A square matrix has the same number of rows as columns, so m=n.
An example of a square matrix is
This matrix has 3 rows and 3 columns: m=n=3.
Identity
Every square dimension set of a matrix has a special counterpart called the "identity matrix", represented by the symbol 
is an identity matrix. There is exactly one identity matrix for each square dimension set. An identity matrix is special because when multiplying any matrix by the identity matrix, the result is always the original matrix with no change.
Inverse matrix
An inverse matrix is a matrix that, when multiplied by another matrix, equals the identity matrix. For example:


The formula for the inverse of a 2x2 matrix, 

Where 

One column matrix
A matrix, that has many rows, but only one column, is called a column vector.
Determinants
The determinant takes a square matrix and calculates a simple number, a scalar. To understand what this number means, take each column of the matrix and draw it as a vector. The parallelogram drawn by those vectors has an area, which is the determinant. For all 2x2 matrices, the formula is very simple: 
For 3x3 matrices the formula is more complicated: 
There are no simple formulas for the determinants of larger matrices, and many computer programmers study how to get computers to quickly find large determinants.
Properties of determinants
There are three rules that all determinants follow. These are:
- The determinant of an identity matrix is 1
- If two rows or two columns of the matrix are exchanged, then the determinant is multiplied by -1. Mathematicians call this alternating.
- If all the numbers in one row or column are multiplied by another number n, then the determinant is multiplied by n. Also, if a matrix M has a column v that is the sum of two column matrices
and
, then the determinant of M is the sum of the determinants of M with
in place of v and M with
in place of v. These two conditions are called multi-linearity.
Related pages
References
Other websites



- History
- MacTutor: Matrices and determinants Archived 2015-03-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Matrices and Linear Algebra on the Earliest Uses Pages
- Earliest Uses of Symbols for Matrices and Vectors
- Online books
- Kaw, Autar K. (September 2008), Introduction to Matrix Algebra, ISBN 978-0-615-25126-4
- Brookes, M. (2005), The Matrix Reference Manual, London: Imperial College, retrieved 2008-12-10
- Online Calculus Courses Archived 2018-07-08 at the Wayback Machine
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Matrix (mathematics), which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.











