Angle Turn
One turn (symbol tr or pla or N) is a unit of plane angle measurement equal to 2π radians, 360 degrees or 400 gradians.
Thus it is the angular measure subtended by a complete circle at its center. As an angular unit, one turn also corresponds to one cycle (symbol cyc or c) or to one revolution (symbol rev or r). Common related units of frequency are cycles per second (cps) and revolutions per minute (rpm). The angular unit of the turn is useful in connection with, among other things, electromagnetic coils (e.g., transformers), rotating objects, and the winding number of curves.
| Turn | |
|---|---|
 Counterclockwise rotations about the center point where a complete rotation corresponds to an angle of rotation of 1 turn. | |
| General information | |
| Unit of | Plane angle |
| Symbol | tr, pla, rev, cyc |
| Conversions | |
| 1 tr in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| radians | 2π rad ≈ 6.283185307... rad |
| milliradians | 2000π mrad ≈ 6283.185307... mrad |
| degrees | 360° |
| gradians | 400g |
In the ISQ, an arbitrary "number of turns" (also known as "number of revolutions" or "number of cycles") is formalized as a dimensionless quantity called rotation, defined as the ratio of a given angle and a full turn. It is represented by the symbol N. Subdivisions of a turn include half-turns and quarter-turns, spanning a semicircle and a right angle, respectively; metric prefixes can also be used as in, e.g., centiturns (ctr), milliturns (mtr), etc.
Another common unit for representing angles is radians, which are usually stated in terms of (pi). The symbol , as representing one half-turn, was developed by William Jones in 1706 and then popularized by Leonhard Euler. In 2010, Michael Hartl proposed instead using the symbol (tau), equal to and corresponding to one turn, for greater conceptual simplicity. This proposal did not initially gain widespread acceptance in the mathematical community, but the constant has become more widespread, having been added to several major programming languages and calculators.
Unit symbols
"N" in the ISQ and SI units
| Rotation | |
|---|---|
Other names | number of revolutions, number of cycles, number of turns, number of rotations |
Common symbols | N |
| SI unit | Unitless |
| Dimension | 1 |
A concept related to the angular unit "turn", defined by the International System of Quantities (ISQ) and adopted in the International System of Units (SI) is the physical quantity rotation (symbol N) defined as number of revolutions:
N is the number (not necessarily an integer) of revolutions, for example, of a rotating body about a given axis. Its value is given by:
- N = φ/2π rad
where φ denotes the measure of rotational displacement.
The above definition is part of the International System of Quantities (ISQ), formalized in the international standard ISO 80000-3 (Space and time), and adopted in the International System of Units (SI). In the ISQ/SI, rotation is used to derive rotational frequency, n=dN/dt, with SI base unit of reciprocal seconds (s-1); common related units of frequency are hertz (Hz), cycles per second (cps), and revolutions per minute (rpm).
| Revolution | |
|---|---|
| Unit of | Rotation |
| Symbol | rev, r, cyc, c |
| Conversions | |
| 1 rev in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| Base units | 1 |
The superseded version ISO 80000-3:2006 defined "revolution" as a special name for the dimensionless unit "one", which also received other special names, such as the radian. Despite their dimensional homogeneity, these two specially named dimensionless units are applicable for non-comparable kinds of quantity: rotation and angle, respectively. "Cycle" is also mentioned in ISO 80000-3, in the definition of period.
"pla" in the EU and Switzerland
The German standard DIN 1315 (March 1974) proposed the unit symbol "pla" (from Latin: plenus angulus 'full angle') for turns. Covered in DIN 1301-1 (October 2010), the so-called Vollwinkel ('full angle') is not an SI unit. However, it is a legal unit of measurement in the EU and Switzerland.
"tr" in calculators
The scientific calculators HP 39gII and HP Prime support the unit symbol "tr" for turns since 2011 and 2013, respectively. Support for "tr" was also added to newRPL for the HP 50g in 2016, and for the hp 39g+, HP 49g+, HP 39gs, and HP 40gs in 2017. An angular mode TURN was suggested for the WP 43S as well, but the calculator instead implements "MULπ" (multiples of π) as mode and unit since 2019.
Proposals for a single letter to represent 2π
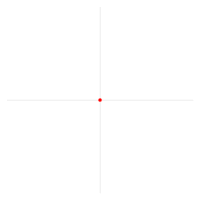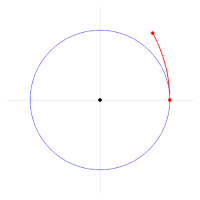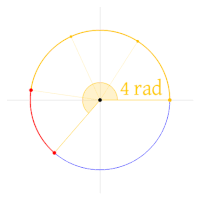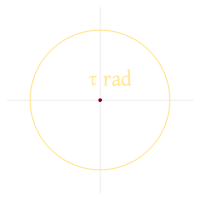
The meaning of the symbol 
In 2001, Robert Palais proposed instead using the number of radians in a turn as the fundamental circle constant instead of π, which amounts to the number of radians in half a turn, in order to make mathematics simpler and more intuitive. His proposal used a "π with three legs" symbol to denote the constant (
In 2008, Thomas Colignatus proposed the uppercase Greek letter theta, Θ, to represent 2π. The Greek letter theta derives from the Phoenician and Hebrew letter teth, 𐤈 or ט, and it has been observed that the older version of the symbol, which means wheel, resembles a wheel with four spokes. It has also been proposed to use the wheel symbol, teth, to represent the value 2π, and more recently a connection has been made among other ancient cultures on the existence of a wheel, sun, circle, or disk symbol—i.e. other variations of teth—as representation for 2π.
In 2010, Michael Hartl proposed to use the Greek letter tau to represent the circle constant: τ = 2π. He offered two reasons. First, τ is the number of radians in one turn, which allows fractions of a turn to be expressed more directly: for instance, a 3/4 turn would be represented as 3τ/4 rad instead of 3π/2 rad. Second, τ visually resembles π, whose association with the circle constant is unavoidable. Hartl's Tau Manifesto gives many examples of formulas that are asserted to be clearer where τ is used instead of π, such as a tighter association with the geometry of Euler's identity using eiτ = 1 instead of eiπ = −1.
Initially, neither of these proposals received widespread acceptance by the mathematical and scientific communities. However, the use of τ has become more widespread, for example:
- In 2012, the educational website Khan Academy began accepting answers expressed in terms of τ.
- The constant τ is made available in the Google calculator, Desmos graphing calculator and in several programming languages such as Python, Raku, Processing, Nim, Rust, GDScript, UE Blueprints, Java, and .NET.
- It has also been used in at least one mathematical research article, authored by the τ-promoter Peter Harremoës.
The following table shows how various identities appear when τ = 2π is used instead of π. For a more complete list, see List of formulae involving π.
| Formula | Using π | Using τ | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angle subtended by 1/4 of a circle | π/2 rad | τ/4 rad | τ/4 rad = 1/4 turn |
| Circumference C of a circle of radius r | C = 2πr | C = τr | |
| Area of a circle | A = πr2 | A = τ r2/2 | The area of a sector of angle θ is A = θ r2/2. |
| Area of a regular n-gon with unit circumradius | A = n/2 sin 2π/n | A = n/2 sin τ/n | |
| n-ball and n-sphere volume recurrence relation | Vn(r) = r/n Sn−1(r) Sn(r) = 2πr Vn−1(r) | Vn(r) = r/n Sn−1(r) Sn(r) = τr Vn−1(r) | V0(r) = 1 S0(r) = 2 |
| Cauchy's integral formula |  |  | |
| Standard normal distribution |  |  | |
| Stirling's approximation |  |  | |
| Euler's identity | eiπ = −1 eiπ + 1 = 0 | eiτ = 1 eiτ − 1 = 0 | For any integer k, eikτ = 1 |
| nth roots of unity |  |  | |
| Planck constant |  |  | ħ is the reduced Planck constant. |
| Angular frequency |  |  |
Subdivisions
A turn can be divided in 100 centiturns or 1000 milliturns, with each milliturn corresponding to an angle of 0.36°, which can also be written as 21′ 36″. A protractor divided in centiturns is normally called a "percentage protractor".
While percentage protractors have existed since 1922, the terms centiturns, milliturns and microturns were introduced much later by the British astronomer Fred Hoyle in 1962. Some measurement devices for artillery and satellite watching carry milliturn scales.
Binary fractions of a turn are also used. Sailors have traditionally divided a turn into 32 compass points, which implicitly have an angular separation of 1/32 turn. The binary degree, also known as the binary radian (or brad), is 1/256 turn. The binary degree is used in computing so that an angle can be represented to the maximum possible precision in a single byte. Other measures of angle used in computing may be based on dividing one whole turn into 2n equal parts for other values of n.
Unit conversion


One turn is equal to 2π (≈ 6.283185307179586) radians, 360 degrees, or 400 gradians.
| Turns | Radians | Degrees | Gradians | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 turn | 0 rad | 0° | 0g | |
| 1/72 turn | 𝜏/72 rad | π/36 rad | 5° | 5+5/9g |
| 1/24 turn | 𝜏/24 rad | π/12 rad | 15° | 16+2/3g |
| 1/16 turn | 𝜏/16 rad | π/8 rad | 22.5° | 25g |
| 1/12 turn | 𝜏/12 rad | π/6 rad | 30° | 33+1/3g |
| 1/10 turn | 𝜏/10 rad | π/5 rad | 36° | 40g |
| 1/8 turn | 𝜏/8 rad | π/4 rad | 45° | 50g |
| 1/2π turn | 1 rad | c. 57.3° | c. 63.7g | |
| 1/6 turn | 𝜏/6 rad | π/3 rad | 60° | 66+2/3g |
| 1/5 turn | 𝜏/5 rad | 2π/5 rad | 72° | 80g |
| 1/4 turn | 𝜏/4 rad | π/2 rad | 90° | 100g |
| 1/3 turn | 𝜏/3 rad | 2π/3 rad | 120° | 133+1/3g |
| 2/5 turn | 2𝜏/5 rad | 4π/5 rad | 144° | 160g |
| 1/2 turn | 𝜏/2 rad | π rad | 180° | 200g |
| 3/4 turn | 3𝜏/4 rad | 3π/2 rad | 270° | 300g |
| 1 turn | 𝜏 rad | 2π rad | 360° | 400g |
See also
- Ampere-turn
- Hertz (modern) or Cycle per second (older)
- Angle of rotation
- Revolutions per minute
- Repeating circle
- Spat (angular unit) – the solid angle counterpart of the turn, equivalent to 4π steradians.
- Unit interval
- Divine Proportions: Rational Trigonometry to Universal Geometry
- Modulo operation
- Twist (mathematics)
Notes
References
External links
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Turn (angle), which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.

