Pylorus
The pylorus (/paɪˈlɔːrəs/ or /pɪˈloʊrəs/) pyloric region or pyloric part connects the stomach to the duodenum.
The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the pyloric antrum (opening to the body of the stomach) and the pyloric canal (opening to the duodenum). The pyloric canal ends as the pyloric orifice, which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the pyloric sphincter. The word pylorus comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word pylorus in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" (Greek: pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word "pylon".
| Pylorus | |
|---|---|
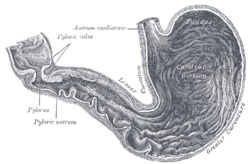 Inside of the stomach (pylorus labeled at center left) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pylorus |
| MeSH | D011708 |
| TA98 | A05.5.01.017 |
| TA2 | 2930 |
| FMA | 14581 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure

* 1. Body of stomach
* 2. Fundus
* 3. Anterior wall
* 4. Greater curvature
* 5. Lesser curvature
* 6. Cardia
* 9. Pyloric sphincter
* 10. Pyloric antrum
* 11. Pyloric canal
* 12. Angular incisure
* 13. Gastric canal
* 14. Rugal folds
The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the antrum, which connects to the body of the stomach, and the pyloric canal, which connects to the duodenum.
Antrum
The antrum also called the gastric antrum or the pyloric antrum is the initial portion of the pyloric region. It is near the bottom of the stomach, proximal to the pyloric sphincter, which separates the stomach and the duodenum. It may temporarily become partially or completely shut off from the remainder of the stomach during digestion by peristaltic contraction of the prepyloric sphincter; it is demarcated, sometimes, from the pyloric canal by a slight groove.
Canal
The pyloric canal (Latin: canalis pyloricus) is the opening between the stomach and the duodenum. The wall thickness of the pyloric canal is up to 3 millimeters (mm) in infants younger than 30 days, and up to 8 mm in adults.
Sphincter
The pyloric sphincter, or valve, is a strong ring of smooth muscle at the end of the pyloric canal which lets food pass from the stomach to the duodenum. It controls the outflow of gastric contents into the duodenum. It receives sympathetic innervation from the celiac ganglion.
Histology

Under microscopy, the pylorus contains numerous glands, including gastric pits, which constitute about half the depth of the pyloric mucosa. They consist of two or three short closed tubes opening into a common duct or mouth. These tubes are wavy, and are about one-half the length of the duct. The duct is lined by columnar cells, continuous with the epithelium lining the surface of the mucous membrane of the stomach, the tubes by shorter and more cubical cell which are finely granular. The glands contain mucus cells and G cells that secrete gastrin.
The pylorus also contains scattered parietal cells and neuroendocrine cells. These endocrine cells include D cells, which release somatostatin, responsible for shutting off acid secretion. (There is a second hormone-sensitive population near the fundus.) Unstriated muscles, which are entirely involuntary, are located at the pylorus.
Function
The pylorus is one component of the gastrointestinal system. Food from the stomach, as chyme, passes through the pylorus to the duodenum. The pylorus, through the pyloric sphincter, regulates entry of food from the stomach into the duodenum.
Clinical significance
In such conditions as stomach cancer, tumours may partly block the pyloric canal. A special tube can be implanted surgically to connect the stomach to the duodenum so as to facilitate the passage of food from one to the other. The surgery to place this tube is called a gastroduodenostomy.
Stenosis
Pyloric stenosis refers to a pylorus that is narrow. This is due to congenital hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter. The lumen of the pylorus is narrower, and less food is able to pass through. This problem is often detected in the early weeks of life. When it is present, a newborn baby may projectile vomit after eating, but despite vomiting remain hungry. Pyloric stenosis may be managed by the insertion of a stent, or through surgical cutting of the pyloric sphincter, a pyloromyotomy.
Other
- Pyloric tumors
- Pyloric gland adenoma
Additional images
- Stomach
- Dissection showing the stomach and pylorus in a cadaver. The antrum of the pylorus is shown in green.
See also
References
External links
- "Pylorus", Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary at Lippincott Williams and Wilkins
- Anatomy photo:37:06-0105 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Abdominal Cavity: The Stomach"
- Anatomy photo:38:07-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver: The Pylorus"
- Anatomy image:8150 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Pylorus, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.

