Petrol Engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American and Canadian English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline).
Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as E10 and E85).

Most petrol engines use spark ignition, unlike diesel engines which typically use compression ignition. Another key difference to diesel engines is that petrol engines typically have a lower compression ratio.
History
The first practical petrol engine was built in 1876 in Germany by Nicolaus August Otto, although there had been earlier attempts by Étienne Lenoir in 1860, Siegfried Marcus in 1864 and George Brayton in 1876.[citation needed]
Design
Thermodynamic cycle
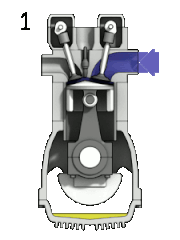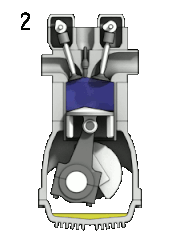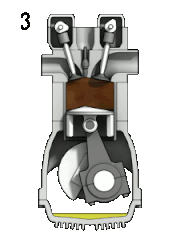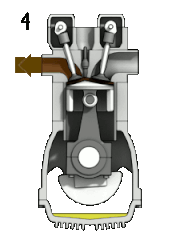
Most petrol engines use either the four-stroke Otto cycle or the two-stroke cycle. Petrol engines have also been produced using the Miller cycle and Atkinson cycle.
Layout
Most petrol-powered piston engines are straight engines or V engines. However, flat engines, W engines and other layouts are sometimes used.
Wankel engines are classified by the number of rotors used.
Compression ratio
Cooling
Petrol engines are either air-cooled or water-cooled.
Ignition
Petrol engines use spark ignition. High voltage for the spark this may be provided by a magneto or an ignition coil. In modern car engines, the ignition timing is managed by an electronic Engine Control Unit. Ignition modules can also function as a rev limiter in some cases to prevent overrevving and the consequences of it, such as valve float and connecting rod failure.
Primer
Primers may be used to help start the engine. They can draw fuel from fuel tanks and vaporize fuel directly into piston cylinders. Engines are difficult to start during cold weather, and the fuel primer helps because otherwise there will not be enough heat available to vaporize the fuel in the carburetor.
Power output and efficiency
The power output of small- and medium-sized petrol engines (along with equivalent engines using other fuels) is usually measured in kilowatts or horsepower.
Typically, petrol engines have a thermodynamic efficiency of about 20-30% (approximately half that of some diesel engines).
Applications
Applications of petrol engines include automobiles, motorcycles, aircraft, motorboats and small engines (such as lawn mowers, chainsaws and portable generators). Petrol engines have also been used as "pony engines", a type of engine used to start a larger, stationary diesel engine.
See also
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Petrol engine, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.