Pancreatic Pseudocyst
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and non-necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the abdomen.
Pancreatic pseudocysts are usually complications of pancreatitis, although in children they frequently occur following abdominal trauma. Pancreatic pseudocysts account for approximately 75% of all pancreatic masses.
| Pancreatic pseudocyst | |
|---|---|
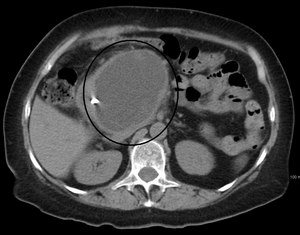 | |
| A pancreatic pseudocyst as seen on CT | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite |
| Complications | Infection, hemorrhage, obstruction |
| Causes | Pancreatitis (chronic), Pancreatic neoplasm |
| Diagnostic method | Cyst fluid analysis |
| Differential diagnosis | Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| Treatment | Cystogastrostomy |
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pancreatic pseudocyst include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite.
Complications
Complications of pancreatic pseudocysts include infection, hemorrhage, obstruction and rupture. For obstruction, it can cause compression in the GI tract from the stomach to colon, compression in urinary system, biliary system, and arteriovenous system.[medical citation needed]
Causes
Pancreatic pseudocyst can occur due to a variety of reasons, among them pancreatitis (chronic), pancreatic neoplasm and/or pancreatic trauma.
Pathophysiology
Pancreatic pseudocysts are sometimes called false cysts because they do not have an epithelial lining. The wall of the pseudocyst is vascular and fibrotic, encapsulated in the area around the pancreas. Pancreatitis or abdominal trauma can cause its formation. Treatment usually depends on the mechanism that brought about the pseudocyst. Pseudocysts take up to 6 weeks to completely form.
Diagnosis

Diagnosis of pancreatic pseudocyst can be based on cyst fluid analysis:
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CA-125 (low in pseudocysts and elevated in tumors);
- Fluid viscosity (low in pseudocysts and elevated in tumors);
- Amylase (usually high in pseudocysts and low in tumors)
The most useful imaging tools are:
- Ultrasonography – the role of ultrasonography in imaging the pancreas is limited by patient habitus, operator experience and the fact that the pancreas lies behind the stomach (and so a gas-filled stomach will obscure the pancreas).
- Computerized tomography – this is the gold standard for initial assessment and follow-up.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) – to establish the relationship of the pseudocyst to the pancreatic ducts, though not routinely used
Treatment

Pancreatic pseudocyst treatment should be aimed at avoiding any complication (1 in 10 cases become infected). They also tend to rupture, and have shown that larger cysts have a higher likelihood to become more symptomatic, even needing surgery. If no signs of infection are present, initial treatment may include conservative measures such as bowel rest (NPO), parenteral nutrition (TPN), and observation. If symptoms do not improve, then endoscopic drainage may be necessary. The majority of pseudocysts can be treated endoscopically; surgical intervention is rarely necessary.
In the event of surgery:
- Cystogastrostomy: In this surgical procedure a connection is created between the back wall of the stomach and the cyst such that the cyst drains into the stomach.
- Cystojejunostomy: In this procedure a connection is created between the cyst and the small intestine so that the cyst fluid directly into the small intestine.
- Cystoduodenostomy: In this procedure a connection is created between the duodenum (the first part of the intestine) and the cyst to allow drainage of the cyst content into duodenum. The type of surgical procedure depends on the location of the cyst. For pseudocysts that occur in the head of the pancreas a cystoduodenostomy is usually performed.
See also
References
Further reading
- Beger, Hans G.; Buchler, Markus; Kozarek, Richard; Lerch, Markus; Neoptolemos, John P.; Warshaw, Andrew; Whitcomb, David; Shiratori, Keiko (2009-01-26). The Pancreas: An Integrated Textbook of Basic Science, Medicine, and Surgery. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444300130.
- Habashi, Samir; Draganov, Peter V (2009). "Pancreatic pseudocyst". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 15 (1): 38–47. doi:10.3748/wjg.15.38. ISSN 1007-9327. PMC 2653285. PMID 19115466.
- Braden, Barbara; Dietrich, Christoph F (2014). "Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts and walled-off necrosis: New technical developments". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (43): 16191–6. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16191. ISSN 2219-2840. PMC 4239507. PMID 25473173.
External links
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Pancreatic pseudocyst, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.
