Huna People
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: Hūṇā) was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century.
The Hunas occupied areas as far south as Eran and Kausambi, greatly weakening the Gupta Empire. The Hunas were ultimately defeated by a coalition of Indian princes that included an Indian king Yasodharman and the Gupta emperor, Narasimhagupta. They defeated a Huna army and their ruler Mihirakula in 528 CE and drove them out of India. The Guptas are thought to have played only a minor role in this campaign.
| Hunas | |
|---|---|
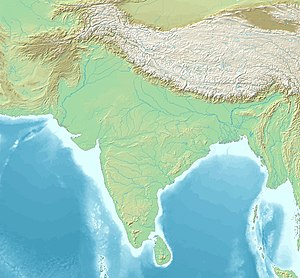
Approximate extent of the Alchon Huns, and find spots of inscriptions related to their local control (map of the Indian subcontinent) | |
| Region | Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Bihar, Sindh, Gilgit-Baltistan, Nuristan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan, Maharashtra, Delhi |
The Hunas are thought to have included the Xionite and/or Hephthalite, the Kidarites, the Alchon Huns (also known as the Alxon, Alakhana, Walxon etc.) and the Nezak Huns. Such names, along with that of the Harahunas (also known as the Halahunas or Harahuras) mentioned in Hindu texts, have sometimes been used for the Hunas in general; while these groups (and the Iranian Huns) appear to have been a component of the Hunas, such names were not necessarily synonymous. Some authors suggest that the Hunas were Ephthalite Huns from Central Asia. The relationship, if any, of the Hunas to the Huns, a Central Asian people who invaded Europe during the same period, is also unclear.
In its farthest geographical extent in India, the territories controlled by the Hunas covered the region up to Malwa in central India. Their repeated invasions and war losses were the main reason for the decline of the Gupta Empire.
History


 Hūṇā) in line 12 (Verse 16) of the Rīsthal inscription, 6th century CE.
Hūṇā) in line 12 (Verse 16) of the Rīsthal inscription, 6th century CE.Chinese sources link the Central Asian tribes comprising the Hunas to both the Xiongnu of north east Asia and the Huns who later invaded and settled in Europe. Similarly, Gerald Larson suggests that the Hunas were a Turkic-Mongolian grouping from Central Asia. The works of Ptolemy (2nd century) are among the first European texts to mention the Huns, followed by the texts by Marcellinus and Priscus. They too suggest that the Huns were an inner Asian people.

The 6th-century Roman historian Procopius of Caesarea (Book I. ch. 3), related the Huns of Europe with the Hephthalites or "White Huns" who subjugated the Sassanids and invaded northwestern India, stating that they were of the same stock, "in fact as well as in name", although he contrasted the Huns with the Hephthalites, in that the Hephthalites were sedentary, white-skinned, and possessed "not ugly" features:
The Ephthalitae Huns, who are called White Huns [...] The Ephthalitae are of the stock of the Huns in fact as well as in name, however they do not mingle with any of the Huns known to us, for they occupy a land neither adjoining nor even very near to them; but their territory lies immediately to the north of Persia [...] They are not nomads like the other Hunnic peoples, but for a long period have been established in a goodly land... They are the only ones among the Huns who have white bodies and countenances which are not ugly. It is also true that their manner of living is unlike that of their kinsmen, nor do they live a savage life as they do; but they are ruled by one king, and since they possess a lawful constitution, they observe right and justice in their dealings both with one another and with their neighbours, in no degree less than the Romans and the Persians
The Kidarites, who invaded Bactria in the second half of the 4th century, are generally regarded as the first wave of Hunas to enter Indian Subcontinent.
The Gupta empire under Skandagupta in the 5th century had successfully repulsed one Hun attack in the northwest in 460 CE. However, over the period of the next several years, the Hunas under successive kings were able to make inroads into the subcontinent.
They were initially based in the Oxus basin in Central Asia and established their control over Gandhara in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent by about 465 CE. From there, they fanned out into various parts of northern, western, and central India. The Hūṇas are mentioned in several ancient texts such as the Rāmāyaṇa, Mahābhārata, Purāṇas, and Kalidasa’s Raghuvaṃśa.
In 528 CE, another campaign led by a coalition of Indian kings finally defeated king Mihirakula and his Huna army. The victory was inscribed on a stone pillar and erected in honor of (and in praise for) one of the leaders of the coalition, king Yashodharman, in Mandasaur in Central India. Huna kings in this inscription are described as 'rude and cruel'. They were also responsible for the destruction of Buddhist monasteries and centers of learning in the Northwest regions of the country.
The Mongolian-Tibetan historian Sumpa Yeshe Peljor (writing in the 18th century) lists the Hunas alongside other peoples found in Central Asia since antiquity, including the Yavanas (Greeks), Kambojas, Tukharas, Khasas and Daradas.
Gurjara-Pratiharas

The Gurjara-Pratiharas suddenly emerged as a political power in north India around sixth century CE, shortly after the Hunas invasion of that region. The Gujara-Pratihara were "likely" formed from a fusion of the Alchon Huns ("White Huns") and native Indian elements, and can probably be considered as a Hunnic state, although its precise origins remain unclear.
Religion
The religious beliefs of the Hunas is unknown, and believed to be a combination of ancestor worship, totemism and animism.
Song Yun and Hui Zheng, who visited the chief of the Hephthalite nomads at his summer residence in Badakshan and later in Gandhara, observed that they had no belief in the Buddhist law and served a large number of divinities."
Gallery
- Victory pillar of Yashodharman at Sondani, Mandsaur claiming victory over the Huns.
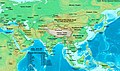
- Asia in 500 CE, showing the Huna domain at its greatest extent.
- Alchon Huns king Khingila.
- Nezak Huns king Napki Malka.
See also
Notes
References
- Iaroslav Lebedynsky, "Les Nomades", Paris 2007, ISBN 978-2-87772-346-6
- Puri, Baij Nath (1957), The history of the Gurjara-Pratihāras, Munshiram Manoharlal
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Huna people, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.