Drinking Straw
A drinking straw is a utensil that is intended to carry the contents of a beverage to one's mouth.
Disposable straws are commonly made from plastics. However, environmental concerns related to plastic pollution and new regulation have led to rise in reusable and biodegradable straws. Following a rise in regulation and public concern, some companies have even voluntarily banned or reduced the number of plastic straws used. Alternative straws are often made of reusable materials like silicone or metal or alternative disposable and biodegradable materials like paper, cardboard, pasta, or bamboo.

A straw is used by placing one end in one's mouth and the other in a beverage. By employing suction, the air pressure in one's mouth drops causing atmospheric pressure to force the liquid through the straw and into the mouth. Drinking straws can be straight or have an angle-adjustable bellows segment. Straws have been used since earliest recorded history, with the first extant straws dating from the 4th century BCE. Different traditional drinks and foods use straws designed for explicit purposes, such as the "straw and sieve" bombilla used to drink the mate infusion common to South America. Since the early 20th century, mass-production of straws from plastic and other industrial products such as cellophane has increased the widespread availability of disposable straws.
Though most straws are used by able-bodied peoples, they play an important role in food and drink access for people with physical disabilities that affect their ability to swallow, hold glassware, or carry the weight of drinks or other liquids. Straws can also be an important part of both child and elderly care or in recovery from certain medical procedures such as dental work, making it safer and easier to consume liquids. Although, the use of straws may not always be advisable depending on the health situation.
History
Early examples
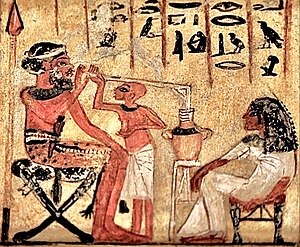
The first known straws were made by the Sumerians and were used for drinking beer, probably to avoid the solid byproducts of fermentation that sink to the bottom. The oldest drinking straw in existence, found in a Sumerian tomb dated 3,000 BCE, was a gold tube inlaid with the precious blue stone lapis lazuli. Others claim metal ‘sceptres’ discovered in Armenia in 1897 and date to the Maykop culture (3700 to 2900 BCE) as the oldest surviving straws.

In the 1800s, the rye grass straw came into fashion because it was cheap and soft, but it had an unfortunate tendency to turn to mush when put in liquid.

American Marvin C. Stone patented the modern drinking straw, 8+1⁄2 inches long and made of paper, in 1888, to address the shortcomings of the rye grass straw. He came upon the idea while drinking a mint julep on a hot day in Washington, D.C.; the taste of the rye grass straw was mixing with the drink and giving it a grassy taste, which he found unsatisfactory. He wound paper around a pencil to make a thin tube, slid out the pencil from one end, and applied glue between the strips. He later refined it by building a machine that would coat the outside of the paper with wax to hold it together, so the glue would not dissolve in bourbon.
Early paper straws had a narrow bore, to prevent seeds from clogging them. It was common to use two of them, to reduce the effort needed to take each sip.[citation needed]
Mass production
Plastic straws became widespread following World War II. The materials used in their manufacture were inexpensive, and the types of restaurant fare that they accompanied had become more affordable and popular.
In 1930, Otto W. Dieffenbach (Sr.) developed and produced a cellophane drinking straw in Baltimore MD. His company known as Glassips Inc. produced straws for restaurants and other products. One patent dates to 1954. The Sr. Mr. Dieffenbach served as chairman until 1972 and the business, then based in Towson, Maryland. was sold in 1979.
One of the first mass-produced twisted straw was Sip-N-See invented by Milton Dinhofer who later came up with the idea and designs for the chimp in the iconic game, Barrel of Monkeys. Dinhofer originally patented his straw in the shape of a scissor with two loops on top, but Macy's would not carry the straw unless it had a character on it. They suggested Dinhofer make three straws (eventually patented in 1950): a cowboy, a clown and an animal for which he made an elephant. Each of his characters was attached to a looping soft polyethylene straw, and users were to sip from another detachable, small, straight, straw of acetate. Rexor Corp. copyrighted the straw the same year, but Macy's decided not to carry them. Dinhofer first marketed the straws with Woolworths. The straws were sold in individual boxes, and more characters were eventually added. Other buyers began to carry it, too, and it was marketed as an "action drinking toy." Sip-N-See went on to sell approximately six million units, and, a decade later, the s-shape of the arms on the cowboy straw would inspire Dinhofer's monkey design for Barrel of Monkeys.
Types
Drinking straws come in many variations and are manufactured using a variety of materials.
Plastic

The most common form of drinking straw is made of the thermoplastic polymer polypropylene. This plastic is known for its durability, lightness, and ability to be manufactured at a low cost. Other plastic polymers that exhibit these traits include polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
These attributes are what have made the traditional plastic straw ubiquitous in fast food establishments and take-out orders around the world. Additionally, other advantages of plastic straws include their ability to be molded into different shapes and sizes while also being able to withstand a wide range of temperatures without deforming. This is important because straws must be temperature resistant and thermally insulated because they can be used in both hot and cold beverages.

One interesting variation of the plastic straw is the "bendy straw", commonly referred to in the industry as an "articulated straw". This straw has a concertina-type hinge near its top to allow for improved maneuverability of the straw when drinking a beverage, especially from a low angle. The articulated straw was invented by Joseph Friedman in 1937. He quickly developed the straw after he saw his daughter struggling to use a normal straight straw.

Another variation of the plastic straw, the "spoon straw", has a spoon-like tip at the bottom, and is often used with iced slush beverages.
"Stir straws" with a relatively short length and quite a narrow bore are often given along with disposable cups for preparing coffee or tea and serve the primary function of being able to stir in sugar, sweetener, cream, or non-dairy creamer, as well as allowing for sipping a hot beverage. Additionally, boba tea plastic straws with wider openings are commonly used to drink bubble tea, to better accommodate its characteristic tapioca pearls. The tip of these straws is often cut at an angle creating a point which allows one to use the straw to puncture the plastic cover of bubble tea drinks.
Plastic straws can also be embellished with some forms marketed as "crazy straws", having a number of twists and turns at the top. These straws are often marketed and can be entertaining for young children. The crazy straw was invented by Arthur Philip Gildersleeve and patented in 1936.
Reusable

Environmental concerns, stemming from the impact plastic waste has had on the ocean, have led to a rise in reusable straws. Reusable straws are primarily being manufactured out of polylactic acid (PLA), silicone, and metal. Polylactic acid and silicone straws are the most similar in texture and feel to their plastic counterparts, however, they fit into the category of biodegradable polymers. These types of straws have some benefits over other more ecologically conscious straws because they are resistant to disintegrating in one's drink and provide adequate insulation for hot and cold drinks. One manufacturer of silicone straws even claims that their straws can be burned into biodegradable ash.
Metal and glass straws are other reusable alternatives. A "vampire straw" is a large metal drinking straw with a pointed tip that allows it to double as a dagger-like weapon. A man was arrested at Boston Logan International Airport after a vampire straw was confiscated from his carry-on luggage.
Bombilla

A bombilla (Spanish), bomba (Portuguese) or massasa (Arabic) is a type of drinking straw, used to drink mate. In metal bombillas, the lower end is perforated and acts as a metal filter which is used to separate the mate infusion from leaves, stems, and other mate debris, and functions in a similar fashion to the perforated metal screen of a teapot. Filters can be removable and can be opened for cleaning, or they may be permanently fixed to the bombilla stem. Bombillas vary in length but a popular length is approximately 7 inches (18 cm) long.
Traditional bombillas are made of metal alloys such as an alloy of copper and nickel called alpaca silver or German silver, stainless steel, and 800 silver which is used to construct the filter and stem, sometimes combined with a gold plated head. Low-end bombillas are made from hollow-stemmed cane. Silver bombillas are popular. In recent times, the traditional silver bombillas are being replaced by ones made from stainless steel.
Silver bombillas were used by the privileged classes, while those made of straw were used by people of lesser means. Due to the high thermal conductivity of silver, bombillas and gourds made of silver can get very hot fast, requiring caution when drinking hot mate tea to avoid burns.Single-use
Some companies such as Starbucks have moved away from plastic straws. Bamboo straws are sometimes made from the moso bamboo tree (Phyllostachys edulis).
Some companies such as McDonald's have switched to paper and paperboard straws.
Edible
Edible straws have been made out of materials like rice, seaweed, rye, and confectioneries (such as candy).
Flavor straws are a form of drinking straw with a flavoring included, designed to make drinking milk more pleasant for children. They first marketed in the United States in 1956 as Flav-R-Straws. Newer variations of the original idea have been resurrected in forms such as Sipahhs, and Magic Milk Straws that contain hundreds of flavored pellets encased within a stiff plastic straw.
Environmental impact

Plastic drinking straw production contributes a small amount to petroleum consumption, and the used straws become a small part of global plastic pollution when discarded, most after a single use.
Plastic straws are not widely recycled and may continue to pollute various aspects of the environment, including bodies of water and streets due to their lack of proper disposal.
A video of a plastic straw being removed from the nostril of a sea turtle by marine biologist Nathan J. Robinson, filmed by Christine Figgener, quickly spread across all forms of media and spurred the elevation of awareness regarding the potential danger of plastic straws for marine life. The scientist who uploaded the video remarks that it is the emotional pull of the imagery, rather than the significance of the plastic straw itself in the plastic debacle, that garnered such high viewership.
Quantity
One anti-straw advocacy group has estimated that about 500 million straws are used daily in the United States alone—an average 1.6 straws per capita per day. This statistic has been criticized as inaccurate, because it was approximated by Milo Cress, who was nine years old at the time, after surveying straw manufacturers to ask their estimates of the total, which he then averaged. (Further details are unavailable as "being 9, he had not thought to document the process closely.") This figure has been widely cited by major news organizations. Market research firm Freedonia Group estimated the number to be 390 million. Another market research firm Technomic estimated the number to be 170 million, although this number excludes some types of straws.
Plastic straws amounted to 5–7.5% of all waste collected from beaches during the 2017 International Cleanup Event, conducted by Ocean Conservancy, making it a minor contamination source, yet considered easy to avoid. In total, they are less than 0.022% of plastic waste emitted to oceans.
Microplastics
Microplastics pollution is a concern if plastic waste is improperly dumped. If plastic straws are improperly disposed of, they can be transported via water into soil ecosystems, and others, where they break down into smaller, more hazardous pieces than the original plastic straw.
Water can break down plastic waste into microplastic and nanoplastic particles. These particles are capable of transmitting harmful substances or can themselves prove dangerous, as they have been shown to negatively affect the surrounding environment.
Alternatives

Alternatives to plastic straws, some reusable, exist, although they are not always readily available, or deemed to be of sufficient quality for all users (including, in particular, those with a disability). Paper straws have proliferated as a popular alternative, although they are prone to losing their rigidity when soaked inside a beverage, and in some cases are not durable enough for thicker beverages such as milkshakes. Metal straws are more durable, but they are incapable of being bent, can damage teeth or lacerate children or kill adults during falls, and some restaurants have reported them as a target of theft.
Some critics have argued that paper and metal alternatives are no more environmentally-friendly than plastic, citing the environmental impacts of paper and mining, and that paper straws would likely end up in landfills and not be composted. In August 2019, after deploying paper straws in the United Kingdom, McDonald's stated that its straws could not actually be recycled at present, since their thickness "makes it difficult for them to be processed by our waste solution providers". The chain stated that they went towards energy production, and not to landfills.
Polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable plastic, requires 69% fewer fossil fuel resources to produce than plastic, but it requires very specific conditions to break down fully. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), derived from plant oil, is marine biodegradable. In 2021, the manufacturing company Wincup was distributing a PHA product branded as "the Phade straw."
As of 2021 several eco-friendly alternative materials have been tried. Among them are hay straws, bamboo straws, seaweed straws, and straws made from naturally dried fallen coconut leaves.
Greenwashing
Not all attempts to be more environmentally friendly are in earnest, though. In an attempt to artificially boost sales, some groups have been guilty of "greenwashing", or falsely marketing their products as a viable environmentally friendly alternative, when it is actually just as harmful to the environment, or worse. These marketing tactics draw in well-meaning consumers who believe they are helping the environment (often by paying more for a product), when they are instead encouraging these misleading strategies.
To combat this scheme, TerraChoice, an America-based advertising company, crafted a rubric to calculate the amount of greenwashing prevalent in a product. They determined that 95% of products they surveyed at American and Canadian stores are guilty of at least one act of greenwashing.
Plastic straw bans and proposals
In the late 2010s, a movement towards laws banning or otherwise restricting the use of plastic straws and other single-use plastics emerged. Environmental groups have encouraged consumers to object to "forced" inclusion of plastic straws with food service. The movement followed the discovery of plastic particles in oceanic garbage patches and larger plastic waste-reduction efforts that focused on banning plastic bags in some jurisdictions. It has been intensified by viral videos, including one of a plastic straw being removed from a sea turtle's nostril by biologist Nathan J. Robinson and filmed by marine biologist and activist Christine Figgener.
By country
Australia
A single-use plastic ban was introduced in the state of South Australia in 2020. Fast food chain McDonald's promised to phase out plastic straws throughout Australia by 2020.
Brazil
On 5 July 2018, the city of Rio de Janeiro became the first state capital of Brazil to forbid the distribution of plastic straws, "forcing restaurants, coffee shops, bars and the like, beach huts and hawkers of the municipality to use and provide to its customers only biodegradable and/or recyclable paper straws individually".
Canada
In May 2018, the Vancouver city council voted in favor of adopting a "Single Use Reduction Strategy", targeting single-use styrofoam containers and plastic straws. The council approved the first phase of the regulations in November 2019, expected to be in place by April 2020, barring the distribution of single-use straws unless requested (with straws on hand required to be bendable for accessibility reasons). Bubble tea shops will be given a one-year exemption.
In March 2019, Starbucks announced that they would be debuting strawless lids for cold drinks across Toronto as a part of their global environmental aspirations.
In June 2019, in the lead-up to the federal election, prime minister Justin Trudeau announced his intent to enact legislation restricting the use of petroleum-based single-used plastics as early as 2021. In 2023, the ban was overturned by the Federal Court, as it was found to be "unreasonable and unconstitutional".
European Union
In May 2018, the European Union proposed a directive banning a number of single-use plastic items including straws, cotton buds, cutlery, balloon sticks and drink stirrers, in addition to limiting the use other single-use plastics and extending producer responsibility. The EU estimated the plan would avoid 3.4 million tons of carbon emissions, save consumers €6.5 billion, and prevent environmental damage that would cost the equivalent of €22 billion by the year 2030. In October 2018, the European Parliament voted to pass the directive with 571 votes for and 53 votes against, and the directive came into effect on 2 July 2021. The specificity of the European market is that it prohibits all types of straws made of plastic, whether bio-based or compostable. This means that popular straws made of PHA, PBS or PLA for example, are prohibited in this territory. It is not always clear whether or not a drinking straw complies with this legislation, so it is recommended that a pyrolysis test be performed to determine its composition.
Taiwan
Single-use plastic straws banned in government facilities, schools, department stores, shopping malls and fast food restaurants from 1 July 2019.
United Kingdom
The UK government committed at most £4 million to "Plastics innovation: towards zero waste" in the summer of 2017 in an attempt to mitigate the circulation of unnecessary plastic. In this endeavor, eleven projects secured the full amount in government support. These projects each invented new ways to recycle used plastic products and prevent them from reaching landfills. In 2018, Queen Elizabeth II banned all single-use plastic items from her palaces.
On 19 April 2018, ahead of Earth Day, a proposal to phase out single-use plastics was announced during the meeting of the Commonwealth Heads of Government. It is estimated that as of 2018, about 23 million straws are used and discarded daily in the UK. In May 2019, England announced that it would ban single-use plastic straws, stirring sticks and cotton buds in April 2020: only registered pharmacies will be allowed to sell straws to the public, and restaurants may only offer them by request of customers. The ban was delayed due to the coronavirus pandemic and came into effect on 1 October 2020.
United States
California
On 7 November 2017, the city of Santa Cruz, California, implemented a ban on all non-recyclable to-go containers, straws, and lids but allowed for 6 months for all businesses to come into compliance before enforcement would occur. On 1 January 2018, the city of Alameda, California, citing the Santa Cruz effort, implemented an immediate ban on all straws, except if requested by a customer, and gave business until 1 July 2018, when it would be required that all straws to be of compostable paper and that all other to-go containers be recyclable.
A statewide California law restricting the providing of single-use plastic straws went into effect on 1 January 2019. Under the law, restaurants are only allowed to provide single-use plastic straws upon request. The law applies to sit-down restaurants but exempts fast-food restaurants, delis, coffee shops, and restaurants that do takeout only. The law does not apply to-go cups and takeaway drinks. A restaurant will receive warnings for its first two violations, then a $25 per day fine for each subsequent violation, up to a maximum of $300 in a year. In a statement released upon his signing the legislation into law, then-Governor Jerry Brown said "It is a very small step to make a customer who wants a plastic straw ask for it. And it might make them pause and think again about an alternative. But one thing is clear, we must find ways to reduce and eventually eliminate single-use plastic products."
Local regulations have also been passed in Malibu, Davis and San Luis Obispo, California.
Florida
Local regulations have been passed in Miami Beach and Fort Myers, Florida.
Maryland
A ban on single-use straws has been instituted in Montgomery County, Maryland, going into full effect on 21 December 2021.
Massachusetts
In 2015, Williamstown, Massachusetts, banned straws that are not recyclable or compostable as part of its Article 42 polystyrene regulations.
In the first half of 2018, three towns in Massachusetts banned petrochemical plastic straws directly in the case of Provincetown, and as part of broader sustainable food packaging laws in Andover and Brookline.
In 2019, Longmeadow, Massachusetts, banned plastic straws and polystyrene packaging.
New York
A drinking straw ban has been proposed in New York City since May 2018. Businesses are fined if a straw is provided (unless requested) and also fined if no plastic straws are available and also fined for other reasons regarding straws.
Washington state
The city of Seattle implemented a ban on non-compostable disposable straws on 1 July 2018.
Voluntary conversions
After consideration of a ban in the UK, in 2018, after a two-month trial of paper straws at a number of outlets in the UK, McDonald's announced they would be switching to paper straws for all locations in the United Kingdom and Ireland. and testing the switch in U.S. locations in June 2018.
A month after the Vancouver ban passed (but before it took effect) Canada's second-largest fast food chain, A&W announced they would have plastic straws fully phased out by January 2019 in all of their locations.
Various independent restaurants have also stopped using plastic straws.
Starbucks announced conversion by 2020 to no-straw lids for all cold drinks except for frappucinos, which will be served with straws made from paper or other sustainable materials.
Hyatt Hotels announced straws would be provided by request only, starting 1 September 2018. Royal Caribbean plans to offer only paper straws on request by 2019, and IKEA said it would eliminate all single-use plastic items by 2020. Other conversions include Waitrose, London City Airport, and Burger King UK stores starting September 2018. A few other cruise lines, air lines, beverage companies, and hotels, have also made partial or complete reductions, but most companies in those industries have not, as of May 2018.
Opposition to bans
Since plastic straws account only for a tiny portion (0.022%) of plastic waste emitted in the oceans each year, some pro-environment critics have argued that plastic straw bans are insufficient to address the issue of plastic waste, and are mostly symbolic.
Full bans on single-use plastic straws have faced opposition from disability rights advocates, as they feel that alternative materials are not well-suited for use by those with impaired mobility (caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy and spinal muscular atrophy). Some with neuromuscular disabilities may rely on a plastic straw for its heat resistance and due to an inability to lift a cup. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) has required public places to provide plastic straws in order to ensure that those who need them will be able to access them. In particular, not all people with disabilities may be capable of washing reusable straws, straws made from inflexible materials are not capable of being repositioned, paper straws lose their firmness over time when soaked in a beverage, and straws made from hard materials such as metal can cause injuries. Advocates have preferred laws that still allow plastic straws to be offered upon request.
The American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC)—a U.S. conservative lobbying group against "excessive" regulation—has promoted model state bills which contain carve-outs for fast food and fast casual restaurants from straw bans (in effect only restricting "sit-down" restaurants), and restrict municipalities from preempting the rule with a stricter regulation (with the draft law text stating that the latter leads to "confusing and varying regulations that could lead to unnecessary increased costs for retail and food establishments to comply with such regulations"). In 2019, the re-election campaign of U.S., Republican Party president Donald Trump marketed packages of reusable plastic straws branded with Trump's name and colored in the signature red associated with the "Make America Great Again" slogan, as a fundraising stunt. The campaign website promoted them as an alternative to "liberal paper straws".
Fiction
In Miguel de Cervantes's novel, Don Quixote (1605, 1615), the narrator tells of an innkeeper who, because Don Quixote refuses to remove his makeshift helmet, fashions a drinking straw by hollowing out a reed and pours wine through it, suggesting that Don Quixote was not accustomed to this method of drinking.
Nicholson Baker's novel, The Mezzanine (1988), includes a detailed discussion of various types of drinking straws experienced by the narrator and their relative merits.
References

- History of beer and bread (and Sumerian straws)
- How plastic drinking straws are made
- #stopsucking campaign Archived 10 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Drinking straw, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.