Wall Street Crash Of 1929: Major American stock market crash
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 was the greatest stock market crash in the history of the United States.

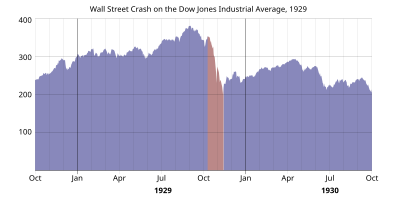
It happened in the New York Stock Exchange on Tuesday October 29, 1929, now known as Black Tuesday. Bank failures followed, resulting in businesses closing. This caused worldwide panic, which started the Great Depression. Stock prices did not reach the same level until late 1954.
The crash signaled the beginning of the 10-year Great Depression that affected all Western industrialized countries. Countries imposed high tariffs and otherwise restricted imports. International trade was on the decline. Soup kitchens were the place to go for food for many people. The Depression ended in the United States with the start of American mobilization for World War II at the end of 1941. People who lost their homes lived in what were Hoovervilles, blaming President Herbert Hoover for the Depression.
The Depression ended as dramatically a decade later on September 3, 1939, when the Second World War began. The widespread poverty and suffering during the 1930s. The Great Depression spread rapidly from the US to Europe and the rest of the world as a result of the connection between the United States and European economies after WWI. The Wall Street Crash was the U.S. Stock Market crash of October 29, 1929, which triggered the Great Depression.
Causes
Stock-exchange speculation led hundreds of thousands of Americans to invest heavily in the stock market, creating an economic bubble. Many were borrowing money to buy more stocks.
"At the turn of the 20th century, stock market speculation was restricted to professionals, but the 1920s saw millions of 'ordinary Americans' investing in the New York Stock Exchange. By August 1929, brokers had lent small investors more than two-thirds of the face value of the stocks they were buying on margin – more than $8.5bn was out on loan".
The amount of money out on loan was more than the entire amount of currency circulating in the US at the time. When a stock price declined below the amount of borrowed money, the owner had to sell to pay the debt. This caused prices to decline more. Years later, regulations limited the use of debt in this way.[source?]
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Wall Street Crash of 1929, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.