Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is a way for people to use the things they need so there will be left.
It means building things without harming the natural world. The Brundtland Commission said sustainable development is the same thing as sustainability: It "meets the needs of the present and [does not] compromise the ability of future generations to meet their own needs""
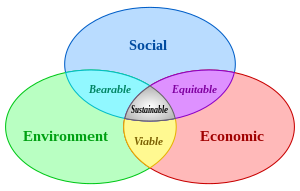
Everyone wants a good place to live. Some people want better homes and housing, while other people want better schools, more jobs, better shops, or cleaner and safer streets. Others may want all these things. What ever the problems in any neighbourhood, they can usually be grouped into three issues. People need:
- A better environment – Green spaces, play areas, no litter, gardens, good houses, less noise and pollution. The resources used should grow back over generations.
- A better economy - Good jobs, reasonable prices, heat and light, no unfair loans
- Better social conditions – Good places to have fun, community groups with sports and arts, friendly neighbours.
Acting against these goals is population growth, which is almost out of control in many countries.
This is not just a local issue. The same problems are faced at a national level. If the governments of the world are to deal with poverty, they do not just need to provide money and food aid, they need to help local people get educated and get jobs. People also need a safe environment with adequate homes and drinking water. To make these things work, governments also need to make sure that people have an effective voice in deciding what happens where they live.
This approach is called "sustainable development". While this phrase can be confusing, it's now used in many government documents and in funding programmes. Sustainable development has three parts: environmental sustainability, economic sustainability and sociopolitical sustainability.
At the core of this idea is the matter of meeting people's needs – for a home, for a decent job, for education for their children, for good health care, and for a safe and healthy neighbourhood to live in.
Most people in the rich nations have most of these needs, but there are still many people living in poverty and in poor quality homes. Even if these basic needs are met there are still plenty of ways in which their ‘quality of life’ is under threat: from crime, from pollution, or from living in neighbourhoods where no-one in authority seems to care.
"Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". - Our Common Future (Report), World Commission on Environment and Development
Many areas have programmes to promote local sustainability: many are called ‘Local Agenda 21’ plans, named after the international Agenda 21 action plan for sustainable development agreed at the United Nations Earth Summit held in 1992.
The UN has released a set of 17 goals aiming at sustainable development. They are:-

Becoming out of date
Population is dropping in many countries. and due to drop in others. Arguments based on population growth are too over-general. What is happening in many countries is a failure to reproduce at replacement rate. This is about 2.1 children on average per female in the population. On average, women are not having so many children as they used to. This is apparently the effect of birth control being available in most countries. Macdonald-ross (talk) 14:11, 9 March 2024 (UTC)
Education for Sustainable Development
Space Education
With the rapid development of science and technology, outer space has become one of the key research objects of various countries since the 20th century. However, because of the uneven development of science and technology, the use of outer space resources varies greatly from country to country, which has led to frequent misuse of outer space resources. Although outer space is not part of the earth's environment, the exploration and use of outer space could have an impact on the earth's ecology, therefore in recent years more and more countries have begun to consider how to more efficiently exploit outer space. It is undoubtedly that education is a wise method for development of sustainable endeavours in outer space. Raising public awareness of outer space, strengthening knowledge of outer space among citizens, and cultivating high-quality elites could provide more possibilities for sustainable work in space in the future.
China National space Administration (CNSA) has selected and listed a number of outer space science education bases, with the aim of continuously integrating high-quality outer space science and technology education resources from all over the country and building a service platform for subsequent education. For example, China has carried out the "China Youth Science Satellite Project" to improve national scientific and technological literacy, train students to have broad international outlook and establish a correct perception of outer space in the context of national basic education reform and international outer space competition. The satellite project, which brings jointly the resources of the Aeroouter space Science and Consortium Schools, enables students to experience the satellite launching process after submitting an application to State Administration of Science, Technology, Industry for National Defence PRC, helping them to think critically about the impact of the launching process on the environment and to further their understanding of outer space. In addition, China also carries out "Space Lecture Programme". Space lectures are mainly conducted by astronauts on the outer space station via satellites transmitting images back to earth for live teaching. Teaching content includes basic knowledge of the universe history and physical science. The live broadcasts are available for global viewing, which is aim to promote equity in outer space education. As of September 2023, China has already conducted four outer space lectures, and the social response has been very positive.
In the United States, in order to stimulate the potential of different students and to cultivate professional researchers for more scientific and environmentally friendly exploration of outer space, NASA has proposed strategy for STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) engagement. NASA STEM Projects consists of "Next Gen STEM", "National Space Grant College and Fellowship Project","Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research" and "Minority University Research and Education Project", which involve a large number of academic faculty, students, and NASA staff. During the program, NASA reorganised educational resources and learning opportunities to include all American students who are interest in outer space, with the aim of reflecting the inclusiveness, richness and equity of the program. The programme not only stimulates the interest of students in outer space to explore a richer pool of talent, but also spreads national outer space knowledge to raise public awareness of outer space development.
European Space Agency (ESA) include the ESA Education Programme in the ESA Convention that is for the development of the next generation of outer space talent. ESA believes that outer space could be of great benefit to STEM education and that all young people deserve equal access to this opportunity for their own development. Therefore, in December 2022, ESA launched "Space for Education 2030" that covers students of all ages to achieve sustainable development of education. Participation in the programme is not restricted by gender, race, ability or background, and students have access to professional guidance, exchange of ideas and creativity through participation in internships or teamwork. The programme has always been in pursuit of educational innovation and is committed to improving the scientific literacy of the next generation in order to cultivate excellence and improve public scientific awareness. At the same time, "Space for Education 2030" is also striving to strengthen the capacity of educators to ensure the quality of teaching and learning so that they could continue to develop innovative pedagogical practices, so as to provide students with broader scope of thinking.
United Nations (UN) has established the United Nations Office for Outer space Affairs (UNOOS) to promote the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) that include quality education. Statistically, 68 % of countries explicitly mention inclusive education, but only 57 % of them mention the education of marginalized groups.. Globally, one in five children has dropped out of school, and children with disabilities account for 15 % of the out-of-school population. Conflicts in the Global South have resulted in a general lack of government attention to education, which are the main reasons for a sharp rise in student dropout rates, poor quality of teaching, and the lack of women's right to education. The project, running until 2030, aims to make efficient use of satellite technology, remote sensing to fill the gap in educational resources. For example, it is beneficial to the development of online education in remote areas through the Internet and the ready access to feedback on educational results. The exist of UNOOOS could play a effective role in improving quality of education all over the world, therefore, it launched a series of initiatives, such as Space4 Women and Space4 Youth to ensure that the quality of education is not affected by the gap between the rich and the poor, racial beliefs and gender and encourage the youth to engage in the aviation in the future.
Related pages
References
Other websites
- Appropedia - a Wiki focused on sustainable international development and poverty reduction
- Sustainable Development in Amazonia
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Sustainable development, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.