Seleucid Empire: Hellenistic-era Greek state in Western Asia (312–63 BC)
The Seleucid Empire was a Hellenistic (or Ancient Greek) successor state of Alexander the Great's empire.
At its greatest extent, the Empire covered central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, Turkmenistan, Pamir and the Indus Valley.
Seleucid Empire | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 312 BC–63 BC | |||||||||||||||||||
Tetradrachm of Seleucus I, the horned horse, the Elephant and the anchor were all used as symbols of the Seleucid monarchy. | |||||||||||||||||||
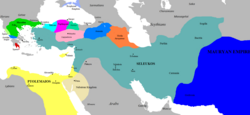 The empire at its greatest extent and on the eve of the death of Seleucus I, 281 BC | |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Seleucia (305–240 BC) Antioch (240–63 BC) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Greek(official) Persian Aramaic | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Olympianism Babylonian religion Zoroastrianism | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Basileus | |||||||||||||||||||
• 305–281 BC | Seleucus I (first) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 65–63 BC | Philip II (last) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Hellenistic period | ||||||||||||||||||
• Wars of the Diadochi | 312 BC | ||||||||||||||||||
• Battle of Ipsus | 301 BC | ||||||||||||||||||
• Roman–Syrian War | 192–188 BC | ||||||||||||||||||
• Treaty of Apamea | 188 BC | ||||||||||||||||||
| 167–160 BC | |||||||||||||||||||
• Annexed by Rome | 63 BC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| 301 BC | 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 240 BC | 2,600,000 km2 (1,000,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 175 BC | 800,000 km2 (310,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 100 BC | 100,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||
Primarily, it was the successor to the Achaemenid Empire of Persia, and was followed there by the Islamic Caliphate (Rashidun Empire) conquest and rule, from 650s to 660s AD. Later on, much of this area became part of the Umayyad Empire and then the Abbasid Empire.
There were over 30 kings of the Seleucid dynasty from 323 to 63 BC.
The partition of Alexander's empire (323–281 BC)
Alexander the Great had conquered the Persian Empire but later died young, leaving his huge empire of partly Hellenized culture without an adult heir.
The empire was put under the management of a regent named Perdiccas in 323 BC, and the territories were divided between Alexander's generals, who thereby became satraps, at the Partition of Babylon. Leaders who thought they should have more, started wars to get it. Soon the various parts of the empire were fighting each other.
The early Seleucid Empire
Seleucus I Nicator was one of Alexander's generals who received a portion of the huge empire Alexander had carved out. He received huge expanses of land in Syria, Babylon, Anatolia, even as far out as India. When Perdiccas was killed in a political assassination by Ptolemy of Egypt, the empire that was barely held together then splintered apart. The Seleucid Empire quickly expanded, eventually taking parts of Thrace in the west and advancing past the Indus in the East.
Seleucus I clashed several times with his southern rival for power, the Ptolemaic Dynasty. The Ptolemaic Dynasty controlled most of Egypt and the lands around it, and would fight the Seleucid Empire on many occasions for control of Syria. Seleucus I conquered much of Anatolia, and was preparing to invade Macedonia, when he was assassinated. This momentarily put an end to the Seleucid Empire's ambitions in Greece. After Seleucus I died, his heirs spent much of their time and money trying to maintain the enormous empire they had inherited. In this, they were rather successful, but the vastness of the empire defied attempts by the successors of Seleucus to control it effectively.
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Seleucid Empire, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.
![Tetradrachm of Seleucus I, the horned horse, the Elephant and the anchor were all used as symbols of the Seleucid monarchy.[1][2] of](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c8/201209071746a_Berlin_Pergamonmuseum%2C_Tetradrachme_Seleukos%27_I%2C_Silber%2C_Pergamon%2C_281-280_v.u.Z.jpg/170px-201209071746a_Berlin_Pergamonmuseum%2C_Tetradrachme_Seleukos%27_I%2C_Silber%2C_Pergamon%2C_281-280_v.u.Z.jpg)