Neutron: Nucleon (constituent of the nucleus of the atom) that has neutral electric charge (no charge); symbol n
Neutrons, with protons and electrons, make up an atom.
Neutrons and protons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Unlike protons, which have a positive charge, or electrons, which have a negative charge, neutrons have zero charge which means they are neutral particles. Neutrons bind with protons with the residual strong force.
Neutrons were predicted by Ernest Rutherford, and discovered by James Chadwick, in 1932. Atoms were fired at a thin pane of beryllium. Particles emerged which had no charge, and he called these 'neutrons'. They were later added to the modern image of the atom.
Neutrons have a mass of 1.675 × 10-24g, which is a little heavier than the proton. Neutrons are 1839 times heavier than electrons.
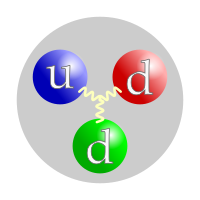
Like all hadrons, neutrons are made of quarks. A neutron is made of two down quarks and one up quark. One up quark has a charge of +2/3, and the two down quarks each have a charge of -1/3. The fact that these charges cancel out is why neutrons have a neutral (0) charge. Quarks are held together by gluons.
Isotopes
Neutrons can be found in almost all atoms together with protons and electrons. Hydrogen-1 is the only exception. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element.
The number of neutrons in an atom does not affect its chemical properties. However it affects its half-life, a measure of its stability. An unstable isotope has a short half-life, in which half of it decays to lighter elements. By contrast, a stable isotope has a long half-life, much longer than that of an unstable isotope. The stability of an isotope is related to radioactivity: an unstable isotope can be highly radioactive.
Atomic reactions
Neutrons are the key to nuclear chain reactions, nuclear power and nuclear weapons.
Related pages
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Neutron, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.
