Red Sea Crisis: Houthi involvement in the Israel–Hamas war
The Red Sea crisis is an ongoing armed conflict in the Middle East.
This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: No reports of events past February 2024. (April 2024) |
It is also known as the United States–Houthi conflict or United States–Iran proxy war. The crisis began on 19 October 2023 after attacks by the Houthi movement. The Houthis are a Shia Islamist insurgent group who control parts of Yemen and are backed by Iran. These attacks target Southern Israel. The Houthis also target ships in the Red Sea that they claimed are linked to Israel or its allies (particularly the United States and United Kingdom).
| Red Sea crisis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of spillover of the Israel–Hamas war, Iran–United States proxy conflict | |||||||
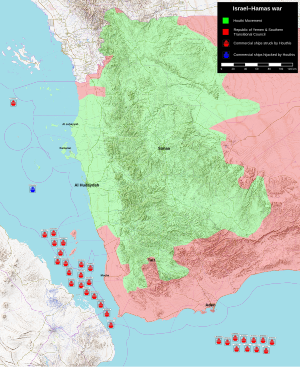 Houthi attacks on commercial ships in the Bab-el-Mandeb strait | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| | Main combatants Operation Prosperity Guardian: | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| |||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Units involved:
Civilian Ships (Non-combatant)
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 43 Houthis killed, 22+ injured | | ||||||
| 1 Yemeni, 1 Vietnamese and 2 Filipinos killed 1 ship and 25 crew members captured Six Egyptian civilians injured One UK-owned cargo ship sunk. | |||||||
Timeline
October 2023
On 19 October 2023, the Houthis launched three land-attack cruise missiles as well as multiple drones towards Israel. According to the U.S. government, these were all shot down by the USS Carney, a destroyer in the United States Navy. This was the first action by the U.S. military to defend Israel during the Israel–Hamas war. Later, it was reported that the Carney had actually shot down four missiles and 15 drones. This action is considered the beginning of the Red Sea Crisis. Later in the day, Saudi Arabia shot down another missile launched by Houthi.
On 27 October, the Houthis fired two drones from the southern Red Sea towards the north. The Israeli military stated the drones were targeted at Israel. One of the two drones fell short, hitting a building next to a hospital in Taba, Egypt. Six people were injured. The other drone fell short and hit near an electricity plant close to the town of Nuweiba, Egypt. After the drone struck Taba, an official for Houthi posted one-word on X; "Eilat". Eilat is the name of a city in Israel.
On 31 October, Houthi attempted a long-range attack on Israel. Houthi launched a ballistic missile and multiple cruise missiles. Israel's Arrow System shot down the ballistic missile. The Israeli Air Force shot down the cruise missiles over the Red Sea. One of the cruise missiles was shot down by an Israeli F-35i Adir fighter jet. This engagement was the first use of the Arrow System during the Israel–Hamas war. The Israeli government also said the interception of the ballistic missile took place above Earth's atmosphere above the Negev Desert. This made it the first instance of space warfare in history.
November 2023
On 1 November, the Israeli military shot down missile fired by Houthi. Houthi had fired the missile towards the city of Eilat, Israel.
On 8 November 2023, Houthi air defenses shot down an American MQ-9 Reaper drone. This resulted in the first American loss of the conflict.
On 9 November, the Houthis fired yet another missile toward the city of Eilat. The missile was shot down by an Israeli Arrow 3 missile. This marked the first time an Arrow 3 missile had been used to shoot down an enemy missile.
On 14 November, the Houthis fired multiple missiles towards Israel. This included one missile aimed at the city of Eilat. The missiles were shot down by Israeli Arrow missiles.
On 15 November, Houthi launched an attack on the USS Thomas Hudner, a destroyer in the United States Navy. The drone was heading towards the destroyer. In self-defense, the Thomas Hudner shot down the Houthi drone.
On 22 November, Houthi once again fired a cruise missile towards the city of Eilat. The missile was shot down by an F35 fighter aircraft in the Israeli Air Force.
On 23 November, Houthi attacked the USS Thomas Hudner again. Houthi launched a series of attack drones towards the Thomas Hudner. All of the drones were shot down, causing no damage to the ship.
On 24 November, Iran attacked the Malta-flagged container ship, CMA CGM Symi. The Iranian military launched a drone towards the ship. The drone was shot down by an Israeli Air Force fighter jet. A drone was shot down over the Red Sea by an IDF fighter jet.
On 29 November, the USS Carney engaged and shot down a Houthi KAS-04. Houthi launched the drone towards the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait.
On 30 November, Saudia Arabia reported that Israel had conducted a military strike against Houthi. The airstrike occurred in Sana'a, the capital of Yemen. Saudia Arabia reported that Israel had struck a Houthi weapons depot. This was denied by Houthi and they reported the Israeli airstrike hit a gas station.
December 2023
On 6 December, Houthi launched military strikes against the Israeli military in the city of Eilat. Houthi launched multiple ballistic missiles towards the Israeli military. None of the missiles hit the military. Also on 6 December, the USS Mason shot down a drone launched by Houthi. The USS Mason is a destroyer in the United States Navy.
On 10 December, the Languedoc, a frigate in the French Navy, shot down two drones launched by Houthi.
On 16 December, the United States Navy shot down 14 drones launched by Houthi. On the same day, the Egyptian Air Defense Forces, a branch of the Egyptian Armed Forces, shot down a object flying around the town of Dahab, Egypt.
On 18 December, the Indian military deployed the INS Kolkata to the Gulf of Aden. The INS Kolkata is a destroyer in the Indian Navy. It was deployed for maritime security. The INS Kochi, another destroyer, was already deployed in the region to stop pirates.
On 26 December, Houthi conducted a series of drone strikes against Israel. Drone strikes were reported over Eilat and other parts of Israel. The United States military shot down 12 Houthi drones. They also shot down five missiles fired by Houthi. Israel also shot down an object launched by Houthi over the Red Sea.
January 2024

On 2 January 2024, the Iranan-backed Houthi movement launched two anti-ship ballistic missiles towards commercial ships in the southern Red Sea. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) conducted an analysis of the attacks and reported the target of the attack was the Malta-flagged container ship CMA CGM TAGE. The missiles landed in the water near the ship, causing no damage. Houthi claimed the CMA CGM TAGE was heading towards Israel, but it was actually heading towards Egypt.
On 6 January, Houthi launched an attack on the USS Laboon. The Laboon is a destroyer in the United States Navy. Three days later on 9 January, Houthi launched a series of drones and missiles at dozens of merchant ships. This caused the United States Navy and the United Kingdom's Navy to respond.
On 9 January 2024, Houthi forces launched 18 one-way suicide drones, two anti-ship cruise missiles, and one anti-ship ballistic missile at dozens of civilian-operated merchant vessels in the Red Sea. These were all shot down by a combined United States and United Kingdom naval force. No damage was reported to any ships.
On 11 January, Houthi failed an attack on the commercial shipping lanes in the Red Sea. Also during the day, the Iranian Navy seized control of the Marshall Islands-flagged, United States-controlled and Greek-operated civilian oil tanker St Nikolas. In the evening of 11 January, The United States seized control and later sunk an Iranian dhow. The dhow was transporting supplies to the Houthi movement. The operation resulted in the entire crew of the vessel being captured. Two U.S. Navy SEALs (or soldiers) were lost at sea. This is the first and currently only casualties the United States suffered during the crisis. On 11 January 2024, the Iranan-backed Houthi movement launched one anti-ship ballistic missiles towards commercial ships in the Gulf of Aden. One commercial ship saw the missile hit the water and reported there was no damage caused by it. This was the 27th attack by Houthi since October 2023.
On 12 January, a coalition launch a large-scale missile attack against the Houthi movement in Yemen. The coalition consisted of the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, Bahrain, Canada and the Netherlands. This attack was the first attack of Operation Poseidon Archer. While retaliating for the airstrikes, Houthi mistakenly targeted the Panama-flagged oil tanker M/T Khalissa. The ship which was carrying oil towards the Russian port of Ust-Luga.
On 14 January, the Iranian backed Houthi movement attacked the USS Laboon, an Arleigh Burke-class destroyer in the United States Navy. At about 4:45 p.m. (Sanaa time), the Houthis launched an anti-ship cruise missile towards the Laboon, which was sailing on the Red Sea. This missile was shot down by an American fighter jet around the coast of Al Hudaydah. There was no damage or injuries as a result of this attack, which occurred just over a week after another attack on the USS Laboon. This attack was also the first U.S.-acknowledged attack by the Houthis since a devastating series of airstrikes by the United States and United Kingdom two days earlier.
On 15 January, the Iranian-backed Houthi movement attacked the Marshall Islands-flagged, United States-owned and operated bulk carrier Gibraltar Eagle. At around 4 p.m. Sanaa time, Houthi launched an anti-ship ballistic missile towards the Gibraltar Eagle. This missile hit the Gibraltar Eagle and caused damage and a fire onboard. Shortly after the attack, Eagle Bulk Shipping, the company that owns the Gibraltar Eagle reported that the ship sustained damage to the cargo hold, but the situation on board was stable.
On 16 January 2024, during the Red Sea Crisis, the Iranian-backed Houthi movement attacked the Maltese-flagged, Greek-owned bulk carrier Zografia in the southern Red Sea. At about 1:45 p.m. Sanaa time, Houthi launched an anti-ship ballistic missile towards the Zografia. The Zografia was struck by the missile, causing damage to the ship. The damage was minor enough for the Zografia to continue their journey.
Houthi brigadier general Yahya Saree posted that the Zografia was fired on because it refused to answer warning calls and was on its way to an Israeli port. The Zografia reported that it was heading for Suez, Egypt, not Israel.
On 17 January, the Iranian-backed Houthi movement attacked the Marshall Islands-flagged, United States-owned and operated bulk carrier Genco Picardy in the Gulf of Aden. According to the United States military, a one-way suicide unmanned aircraft system struck the Genco Picardy at approximately 8:30 pm Sanaa time. The Genco Picardy sustained damage, but remained seaworthy and could continue its journey.
On 17 January, Houthi launched a one-way suicide drone and struck the Marshall Islands-flagged, United States-owned and operated bulk carrier Genco Picardy in the Gulf of Aden.
February 2024
On 3 February, the US and UK bombed 36 Houthi sites in Yemen.
On 10 February, Houthi media announced the names of 17 fighters who were killed in the US-UK strikes.
On 19 February, Houthis claimed they shot down an MQ-9 Reaper drone over the Red Sea. US officials said it's true and added that the drone belonged to the US Air Force and crashed off the coast of Hodeidah.
On 20 February, France announced that one of its warships shot down two Houthi UAVs over the Red Sea.
On 22 February, The Houthis launched drones and ballistic missiles aimed at Eilat and an American destroyer in the Red Sea, but authorities reported that none hit their targets. However, two missiles fired by the Houthis struck a cargo ship named Islander, which carries the flag of Palau. This caused a fire and injured one sailor, but the ship continued its journey. Houthi leader Abdul-Malik al-Houthi stated that operations in the Red Sea and nearby waters were ongoing, growing, and effective. He also announced the use of "submarine weapons," though he did not provide more details on it.
On 24 February, the United States and the United Kingdom carried out their fourth round of joint airstrikes, targeting 18 Houthi sites spread across eight locations. The British Ministry of Defense reported that four Royal Air Force Typhoon fighter jets, with support from two Voyager tankers, were involved in the airstrikes. According to the Houthis' official news agency, the attacks resulted in the death of one civilian and injuries to eight others. This was the first civilian casualties during these joint airstrikes that are conducted by the US and UK on Houthi-ruled territory in Yemen.
On 26 February, the German frigate Hessen launched two SM-2 missiles at an American Reaper drone in a friendly fire incident. The missiles missed their target, falling into the sea.
March 2024
On 4 March, Houthi Telecommunication Minister Misfer Al-Numair stated that ships entering Yemeni waters must have a permit from the Houthi-controlled Maritime Affairs Authority.
Notes
Related pages
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia Simple English article Red Sea crisis, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki Simple English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.