Step Function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals.
Informally speaking, a step function is a piecewise constant function having only finitely many pieces.

Definition and first consequences
A function 
, for all real numbers
where 




In this definition, the intervals 
- The intervals are pairwise disjoint:
for
- The union of the intervals is the entire real line:
Indeed, if that is not the case to start with, a different set of intervals can be picked for which these assumptions hold. For example, the step function
can be written as
Variations in the definition
Sometimes, the intervals are required to be right-open or allowed to be singleton. The condition that the collection of intervals must be finite is often dropped, especially in school mathematics, though it must still be locally finite, resulting in the definition of piecewise constant functions.
Examples

- A constant function is a trivial example of a step function. Then there is only one interval,
- The sign function sgn(x), which is −1 for negative numbers and +1 for positive numbers, and is the simplest non-constant step function.
- The Heaviside function H(x), which is 0 for negative numbers and 1 for positive numbers, is equivalent to the sign function, up to a shift and scale of range (
). It is the mathematical concept behind some test signals, such as those used to determine the step response of a dynamical system.
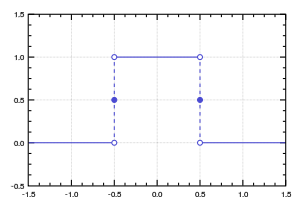
- The rectangular function, the normalized boxcar function, is used to model a unit pulse.
Non-examples
- The integer part function is not a step function according to the definition of this article, since it has an infinite number of intervals. However, some authors also define step functions with an infinite number of intervals.
Properties
- The sum and product of two step functions is again a step function. The product of a step function with a number is also a step function. As such, the step functions form an algebra over the real numbers.
- A step function takes only a finite number of values. If the intervals
for
in the above definition of the step function are disjoint and their union is the real line, then
for all
- The definite integral of a step function is a piecewise linear function.
- The Lebesgue integral of a step function
is
where
is the length of the interval
, and it is assumed here that all intervals
have finite length. In fact, this equality (viewed as a definition) can be the first step in constructing the Lebesgue integral.
- A discrete random variable is sometimes defined as a random variable whose cumulative distribution function is piecewise constant. In this case, it is locally a step function (globally, it may have an infinite number of steps). Usually however, any random variable with only countably many possible values is called a discrete random variable, in this case their cumulative distribution function is not necessarily locally a step function, as infinitely many intervals can accumulate in a finite region.
See also
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Step function, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.







