Nicotinamide
Niacinamide or nicotinamide is a form of vitamin B3 found in food and used as a dietary supplement and medication.
As a supplement, it is used orally (swallowed by mouth) to prevent and treat pellagra (niacin deficiency). While nicotinic acid (niacin) may be used for this purpose, niacinamide has the benefit of not causing skin flushing. As a cream, it is used to treat acne, and has been observed in clinical studies to improve the appearance of aging skin by reducing hyperpigmentation and redness. It is a water-soluble vitamin. Niacinamide is the supplement name, while nicotinamide is the scientific name.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌnaɪəˈsɪnəmaɪd/, /ˌnɪkəˈtɪnəmaɪd/ |
| Other names | NAM, 3-pyridinecarboxamide niacinamide nicotinic acid amide vitamin PP nicotinic amide vitamin B3 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.467 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H6N2O |
| Molar mass | 122.127 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 129.5 °C (265.1 °F) |
| Boiling point | 334 °C (633 °F) |
| |
| |
Side effects are minimal. At high doses, liver problems may occur. Normal amounts are safe for use during pregnancy. Niacinamide is in the vitamin B family of medications, specifically the vitamin B3 complex. It is an amide of nicotinic acid. Foods that contain niacinamide include yeast, meat, milk, and green vegetables.
Niacinamide was discovered between 1935 and 1937. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Niacinamide is available as a generic medication and over the counter. Commercially, niacinamide is made from either nicotinic acid (niacin) or nicotinonitrile. In some countries, grains have niacinamide added to them.
Medical uses
Niacin deficiency
Niacinamide is the preferred treatment for pellagra, caused by niacin deficiency.
Acne
Niacinamide cream is used as a treatment for acne. It has anti-inflammatory actions, which may benefit people with inflammatory skin conditions.
Niacinamide increases the biosynthesis of ceramides in human keratinocytes in vitro and improves the epidermal permeability barrier in vivo. The application of 2% topical niacinamide for 2 and 4 weeks has been found to be effective in lowering the sebum excretion rate. Niacinamide has been shown to prevent Cutibacterium acnes-induced activation of toll-like receptor 2, which ultimately results in the down-regulation of pro-inflammatory interleukin-8 production.
Skin cancer
Niacinamide at doses of 500 to 1000 mg a day decreases the risk of skin cancers, other than melanoma, in those at high risk.
Side effects
Niacinamide has minimal side effects. At very high doses above 3g/ day acute liver toxicity has been documented in at least one case. Normal doses are safe during pregnancy.
Chemistry
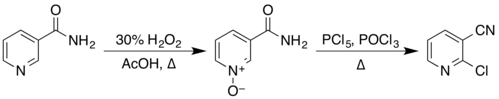
The structure of nicotinamide consists of a pyridine ring to which a primary amide group is attached in the meta position. It is an amide of nicotinic acid. As an aromatic compound, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions and transformations of its two functional groups. Examples of these reactions reported in Organic Syntheses include the preparation of 2-chloronicotinonitrile by a two-step process via the N-oxide,
from nicotinonitrile by reaction with phosphorus pentoxide, and from 3-aminopyridine by reaction with a solution of sodium hypobromite, prepared in situ from bromine and sodium hydroxide.

Industrial production
The hydrolysis of nicotinonitrile is catalysed by the enzyme nitrile hydratase from Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1, producing 3500 tons per annum of nicotinamide for use in animal feed. The enzyme allows for a more selective synthesis as further hydrolysis of the amide to nicotinic acid is avoided. Nicotinamide can also be made from nicotinic acid. According to Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, worldwide 31,000 tons of nicotinamide were sold in 2014.
Biochemistry

Nicotinamide, as a part of the cofactor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH / NAD+) is crucial to life. In cells, nicotinamide is incorporated into NAD+ and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+). NAD+ and NADP+ are cofactors in a wide variety of enzymatic oxidation-reduction reactions, most notably glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. If humans ingest nicotinamide, it will likely undergo a series of reactions that transform it into NAD, which can then undergo a transformation to form NADP+. This method of creation of NAD+ is called a salvage pathway. However, the human body can produce NAD+ from the amino acid tryptophan and niacin without our ingestion of nicotinamide.
NAD+ acts as an electron carrier that mediates the interconversion of energy between nutrients and the cell's energy currency, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In oxidation-reduction reactions, the active part of the cofactor is the nicotinamide. In NAD+, the nitrogen in the aromatic nicotinamide ring is covalently bonded to adenine dinucleotide. The formal charge on the nitrogen is stabilized by the shared electrons of the other carbon atoms in the aromatic ring. When a hydride atom is added onto NAD+ to form NADH, the molecule loses its aromaticity, and therefore a good amount of stability. This higher energy product later releases its energy with the release of a hydride, and in the case of the electron transport chain, it assists in forming adenosine triphosphate.
When one mole of NADH is oxidized, 158.2 kJ of energy will be released.
Biological role
Nicotinamide occurs as a component of a variety of biological systems, including within the vitamin B family and specifically the vitamin B3 complex. It is also a critically important part of the structures of NADH and NAD+, where the N-substituted aromatic ring in the oxidised NAD+ form undergoes reduction with hydride attack to form NADH. The NADPH/NADP+ structures have the same ring, and are involved in similar biochemical reactions.
Nicotinamide can be methylated in the liver to biologically active 1-Methylnicotinamide when there are sufficient methyl donors.
Food sources
Niacinamide occurs in trace amounts mainly in meat, fish, nuts, and mushrooms, as well as to a lesser extent in some vegetables. It is commonly added to cereals and other foods. Many multivitamins contain 20–30 mg of vitamin B3 and it is also available in higher doses.
Compendial status
Research
A 2015 trial found niacinamide to reduce the rate of new nonmelanoma skin cancers and actinic keratoses in a group of people at high risk for the conditions.
Niacinamide has been investigated for many additional disorders, including treatment of bullous pemphigoid nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Niacinamide may be beneficial in treating psoriasis.
There is tentative evidence for a potential role of niacinamide in treating acne, rosacea, autoimmune blistering disorders, ageing skin, and atopic dermatitis. Niacinamide also inhibits poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARP-1), enzymes involved in the rejoining of DNA strand breaks induced by radiation or chemotherapy. ARCON (accelerated radiotherapy plus carbogen inhalation and nicotinamide) has been studied in cancer.
Research has suggested niacinamide may play a role in the treatment of HIV.
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Nicotinamide, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.