List Of Countries By System Of Government
This is a list of sovereign states by constitutionally defined system of government.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
This list does not measure degree of democracy, political corruption, or state capacity of governments.
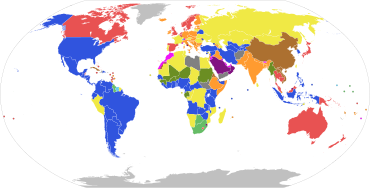
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system: President is the head of government and is independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Note: this chart represent de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.[citation needed]
Parliamentary systems
Constitutional monarchies
These are systems in which the head of state is a constitutional monarch; the existence of their office and their ability to exercise their authority is established and restrained by constitutional law.
Systems in which a prime minister is the active head of the executive branch of government. In some cases, the prime minister is also leader of the legislature, while in other cases the executive branch is clearly separated from legislature (although the entire cabinet or individual ministers must step down in the case of a vote of no confidence).[dubious ] The head of state is a constitutional monarch who normally only exercises his or her powers with the consent of the government, the people and/or their representatives (except in emergencies, e.g. a constitutional crisis or a political deadlock).
 Andorra
Andorra Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Australia
Australia Bahamas
Bahamas Belgium
Belgium Belize
Belize Cambodia
Cambodia Canada
Canada Cook Islands
Cook Islands Denmark
Denmark Grenada
Grenada Jamaica
Jamaica Japan
Japan Lesotho
Lesotho Luxembourg
Luxembourg Malaysia
Malaysia Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Niue
Niue Norway
Norway Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Spain
Spain Sweden
Sweden Thailand
Thailand Tuvalu
Tuvalu United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Parliamentary republics with a ceremonial president
In a parliamentary republic, the head of government is selected or nominated by the legislature and is also accountable to it. The head of state is ordinarily called a president and (in full parliamentary republics) is separate from the head of government, serving a largely apolitical, ceremonial role. In these systems, the head of government is usually called the prime minister, chancellor or premier. In mixed republican systems and directorial republican systems, the head of government also serves as head of state and is usually titled president.
In some full parliamentary systems, the head of state is directly elected by voters. Under other classification systems, however, these systems may instead be classed as semi-presidential systems as presidents are always attached to a political party and may have broad powers (despite their weak presidency). Full parliamentary republican systems with presidents being purely ceremonial and neutral with no broad powers, do not have a directly elected head of state and instead usually use either an electoral college or a vote in the legislature to appoint the president.
Directly elected head of state
Indirectly elected head of state
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
Parliamentary republics with an executive president
A combined head of state and head of government in the form of an executive president is elected by the legislature, and they must maintain the confidence of the legislature to remain in office. In effect, "presidents" in this system function the same as prime ministers do in other parliamentary systems.
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (April 2024) |
Presidential systems
In presidential systems a president is the head of government, and is elected and remains in office independently of the legislature. There is generally no prime minister, although if one exists, in most cases they serve purely at the discretion of the president.
Presidential republics without a prime minister
 Angola
Angola Benin
Benin Bolivia
Bolivia Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cyprus
Cyprus Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador El Salvador
El Salvador Gambia, The
Gambia, The Ghana
Ghana Guatemala
Guatemala Honduras
Honduras Indonesia
Indonesia Iran
Iran Liberia
Liberia Malawi
Malawi Maldives
Maldives Mexico
Mexico Nicaragua
Nicaragua Nigeria
Nigeria Palau
Palau Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay Philippines
Philippines Seychelles
Seychelles Somaliland
Somaliland Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan United States
United States Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
Presidential republics with a prime minister
The following countries have presidential systems where a post of prime minister (official title may vary) exists alongside that of the president. The president is still both the head of state and government and the prime minister's roles are mostly to assist the president.
 Abkhazia
Abkhazia Argentina (see Chief of the Cabinet of Ministers)
Argentina (see Chief of the Cabinet of Ministers) Belarus
Belarus Burundi
Burundi Cameroon
Cameroon Central African Republic
Central African Republic Djibouti
Djibouti Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast Kenya (see Prime Cabinet Secretary)
Kenya (see Prime Cabinet Secretary) Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Senegal
Senegal Sierra Leone (see Chief minister)
Sierra Leone (see Chief minister) South Korea
South Korea Syria
Syria Rwanda
Rwanda Tajikistan
Tajikistan Tanzania
Tanzania Togo
Togo Transnistria
Transnistria Uganda
Uganda Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
Hybrid systems
Semi-presidential republics
In a semi-presidential republic a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature. It differs from a parliamentary system in that it has an executive president independent from legislature; and from the presidential system in that the cabinet, although named by the president, is responsible to the legislature, which may force the cabinet to resign through a motion of no confidence.
Premier-presidential systems
In a premier-presidential system the prime minister and cabinet are exclusively accountable to the legislature.
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
President-parliamentary systems
In a president-parliamentary system the prime minister and cabinet are dually accountable to the president and the legislature.
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
Assembly-independent republics
A combined head of state and head of government (usually titled president) is elected by the legislature but is not held accountable to it (as is their cabinet), thus acting more independently from the legislature. They may or may not also hold a seat in the legislature.
In a directorial republic, a council jointly exercises the powers and ceremonial roles of both the head of state and head of government. The council is elected by the parliament, but is not subject to parliamentary confidence during its fixed term.
Semi-constitutional monarchies
The prime minister is the nation's active executive, but the monarch still has considerable political powers that can be used at their own discretion.
Absolute monarchies
Specifically, monarchies in which the monarch's exercise of power is unconstrained by any substantive constitutional law. The monarch acts as both head of state and head of government.
One-party states
States in which political power is by law concentrated within one political party whose operations are largely fused with the government hierarchy (in contrast to states where a multi-party system formally exists, but this fusion is achieved anyway through election fraud or underdeveloped multi-party traditions).
 China (Communist Party leads eight minor political parties) (list)
China (Communist Party leads eight minor political parties) (list) Cuba (Communist Party) (list)
Cuba (Communist Party) (list) Eritrea (People's Front for Democracy and Justice) (list)
Eritrea (People's Front for Democracy and Justice) (list) North Korea (Workers' Party leads the Democratic Front) (list)
North Korea (Workers' Party leads the Democratic Front) (list) Laos (People's Revolutionary Party leads the Front for National Construction) (list)
Laos (People's Revolutionary Party leads the Front for National Construction) (list) Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (Polisario Front)
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (Polisario Front) Vietnam (Communist Party leads the Fatherland Front) (list)
Vietnam (Communist Party leads the Fatherland Front) (list)
Nations with limited recognition are in italics.
Military juntas
A committee of the nation's military leaders controls the government for the duration of a state of emergency. Constitutional provisions for government are suspended in these states; constitutional forms of government are stated in parentheses.
Provisional governments
States that have a system of government that is in transition or turmoil. These regimes lack a constitutional basis.
Systems of internal structure
Unitary states
A state governed as a single power in which the central government is ultimately supreme and any administrative divisions (sub-national units) exercise only the powers that the central government chooses to delegate. The majority of states in the world have a unitary system of government. Of the 193 UN member states, 126 are governed as centralized unitary states, and an additional 40 are regionalized unitary states.
Centralized unitary states
States in which most power is exercised by the central government. What local authorities do exist have few powers.
Regionalized unitary states
States in which the central government has delegated some of its powers to regional authorities, but where constitutional authority ultimately remains entirely at a national level.
 Azerbaijan (59 districts, and 1 autonomous republic)
Azerbaijan (59 districts, and 1 autonomous republic) Bolivia (9 departments)
Bolivia (9 departments) Chile (16 regions)
Chile (16 regions) People's Republic of China (22 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 province-level municipalities, 2 special administrative regions, and 1 claimed province)
People's Republic of China (22 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 province-level municipalities, 2 special administrative regions, and 1 claimed province) Colombia (34 departments, and 1 capital district)
Colombia (34 departments, and 1 capital district) Denmark (5 regions, and 2 self-governing territories)
Denmark (5 regions, and 2 self-governing territories) Finland (19 regions, and
Finland (19 regions, and  Åland)
Åland) France (18 regions, of which 6 are autonomous)
France (18 regions, of which 6 are autonomous) Georgia (9 regions, and 2 autonomous republics)
Georgia (9 regions, and 2 autonomous republics) Greece (7 decentralized administrations, and 1 autonomous monastic state)
Greece (7 decentralized administrations, and 1 autonomous monastic state) Indonesia (38 provinces, of which 9 have special status)
Indonesia (38 provinces, of which 9 have special status) Israel (6 districts, Judea and Samaria Area)
Israel (6 districts, Judea and Samaria Area) Italy (20 regions, of which 5 are autonomous)
Italy (20 regions, of which 5 are autonomous) Japan (47 prefectures)
Japan (47 prefectures) Kazakhstan (17 regions, 3 cities with region rights)
Kazakhstan (17 regions, 3 cities with region rights) Kenya (47 counties)
Kenya (47 counties) Kingdom of the Netherlands (4 constituent countries)
Kingdom of the Netherlands (4 constituent countries) Mauritania (15 regions)
Mauritania (15 regions) Moldova (32 districts, 3 municipalities, and 2 autonomous territorial units)
Moldova (32 districts, 3 municipalities, and 2 autonomous territorial units) New Zealand (16 regions, 1 self-administering territory, and 2 states in free association)
New Zealand (16 regions, 1 self-administering territory, and 2 states in free association) Nicaragua (15 departments, 2 autonomous regions)
Nicaragua (15 departments, 2 autonomous regions) Norway (10 counties, 1 autonomous city, 2 integral overseas areas, 3 dependencies)
Norway (10 counties, 1 autonomous city, 2 integral overseas areas, 3 dependencies) Papua New Guinea (20 provinces, 1 autonomous region, and 1 national capital district)
Papua New Guinea (20 provinces, 1 autonomous region, and 1 national capital district) Peru (25 regions, and 1 province)
Peru (25 regions, and 1 province) Philippines (one autonomous region subdivided into 5 provinces and 113 other provinces and independent cities grouped into 17 other non-autonomous regions)
Philippines (one autonomous region subdivided into 5 provinces and 113 other provinces and independent cities grouped into 17 other non-autonomous regions) Portugal (18 districts, and 2 autonomous regions)
Portugal (18 districts, and 2 autonomous regions) São Tomé and Príncipe (6 districts, and
São Tomé and Príncipe (6 districts, and  Príncipe)
Príncipe) Serbia (29 districts, 2 autonomous provinces (one of which is a partially recognized de facto independent state), and 1 autonomous city)
Serbia (29 districts, 2 autonomous provinces (one of which is a partially recognized de facto independent state), and 1 autonomous city) Solomon Islands (9 provinces, and 1 capital territory)
Solomon Islands (9 provinces, and 1 capital territory) South Africa (9 provinces)
South Africa (9 provinces) South Korea (8 provinces, 6 special cities, and 1 autonomous province)
South Korea (8 provinces, 6 special cities, and 1 autonomous province) Spain (17 autonomous communities, 15 communities of common-regime, 1 community of chartered regime, 3 chartered provinces, 2 autonomous cities)
Spain (17 autonomous communities, 15 communities of common-regime, 1 community of chartered regime, 3 chartered provinces, 2 autonomous cities) Sri Lanka (9 provinces)
Sri Lanka (9 provinces) Tajikistan (3 regions, 1 autonomous region, and 1 capital city)
Tajikistan (3 regions, 1 autonomous region, and 1 capital city) Tanzania (21 regions, and
Tanzania (21 regions, and  Zanzibar)
Zanzibar) Trinidad and Tobago (9 regions, 1 autonomous island, 3 boroughs, and 2 cities)
Trinidad and Tobago (9 regions, 1 autonomous island, 3 boroughs, and 2 cities) Ukraine (24 oblasts, 2 cities with special status, and
Ukraine (24 oblasts, 2 cities with special status, and  Crimea)
Crimea) United Kingdom (4 countries –
United Kingdom (4 countries –  England,
England,  Scotland, Northern Ireland and
Scotland, Northern Ireland and  Wales, of which 3 have devolved governments – Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales)
Wales, of which 3 have devolved governments – Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales) Uzbekistan (3 regions, 1 autonomous republic, and 1 independent city)
Uzbekistan (3 regions, 1 autonomous republic, and 1 independent city)
Federation
States in which the national government shares power with regional governments with which it has legal or constitutional parity. The central government may or may not be (in theory) a creation of the regional governments.
 Argentina (23 provinces and one autonomous city)
Argentina (23 provinces and one autonomous city) Australia (six states and ten territories)
Australia (six states and ten territories) Austria (nine states)
Austria (nine states) Belgium (three regions and three linguistic communities)
Belgium (three regions and three linguistic communities) Bosnia and Herzegovina (two entities and one district that is a condominium of the two entities)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (two entities and one district that is a condominium of the two entities) Brazil (26 states and the Federal District)
Brazil (26 states and the Federal District) Canada (ten provinces and three territories)
Canada (ten provinces and three territories) Comoros (
Comoros ( Anjouan,
Anjouan,  Grande Comore, and
Grande Comore, and  Mohéli)
Mohéli) Ethiopia (10 regions and 2 chartered cities)
Ethiopia (10 regions and 2 chartered cities) Germany (16 states)
Germany (16 states) India (28 states and 8 union territories)
India (28 states and 8 union territories) Iraq (18 governorates and one region:
Iraq (18 governorates and one region:  Kurdistan)
Kurdistan) Malaysia (13 states and three federal territories)
Malaysia (13 states and three federal territories) Mexico (32 states)
Mexico (32 states) Federated States of Micronesia (
Federated States of Micronesia ( Chuuk,
Chuuk,  Kosrae,
Kosrae,  Pohnpei and
Pohnpei and  Yap)
Yap) Nepal (seven provinces)
Nepal (seven provinces) Nigeria (36 states and one federal territory: Federal Capital Territory)
Nigeria (36 states and one federal territory: Federal Capital Territory) Pakistan (4 provinces, 2 autonomous territories and 1 federal territory)
Pakistan (4 provinces, 2 autonomous territories and 1 federal territory) Russia (46 oblasts, 22 republics (one of which is disputed), nine krais, four autonomous okrugs, three federal cities (one of which is disputed), one autonomous oblast)
Russia (46 oblasts, 22 republics (one of which is disputed), nine krais, four autonomous okrugs, three federal cities (one of which is disputed), one autonomous oblast) Saint Kitts and Nevis (Saint Kitts,
Saint Kitts and Nevis (Saint Kitts,  Nevis)
Nevis) Somalia (six federal member states)
Somalia (six federal member states) South Sudan (ten states)
South Sudan (ten states) Sudan (17 states)
Sudan (17 states) Switzerland (26 cantons)
Switzerland (26 cantons) United Arab Emirates (seven emirates)
United Arab Emirates (seven emirates) United States (50 states, one incorporated territory, and one federal district:
United States (50 states, one incorporated territory, and one federal district:  District of Columbia)
District of Columbia) Venezuela (23 states, one capital district, and the
Venezuela (23 states, one capital district, and the  Federal Dependencies of Venezuela)
Federal Dependencies of Venezuela)
European Union
The exact political character of the European Union is debated, some arguing that it is sui generis (unique), but others arguing that it has features of a federation or a confederation. It has elements of intergovernmentalism, with the European Council acting as its collective "president", and also elements of supranationalism, with the European Commission acting as its executive and bureaucracy.
See also
Notes
References
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article List of countries by system of government, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.






























































































































































































































