D
D, or d, is the fourth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide.
Its name in English is dee (pronounced /ˈdiː/), plural dees.
| D | |
|---|---|
| D d | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Phonetic usage | |
| Unicode codepoint | U+0044, U+0064 |
| Alphabetical position | 4 Numerical value: 4 |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Time period | ~-700 to present |
| Descendants | |
| Sisters | |
| Other | |
| Other letters commonly used with | d(x) |
| Associated numbers | 4 |
| Writing direction | Left-to-Right |
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph door, fish | Phoenician daleth | Western Greek Delta | Etruscan D | Latin D | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|  |  |  |  |
The Semitic letter Dāleth may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are many different Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek and Latin, the letter represented /d/; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was archaic, but still retained (see letter B). The equivalent Greek letter is Delta, Δ.
The minuscule (lower-case) form of 'd' consists of a lower-story left bowl and a stem ascender. It most likely developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form 'D', and today now composed as a stem with a full lobe to the right. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This serif was extended while the rest of the letter was reduced, resulting in an angled stroke and loop. The angled stroke slowly developed into a vertical stroke.
Use in writing systems
| Languages in italics are not usually written using the Latin alphabet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Dialect(s) | Pronunciation (IPA) | Environment | Notes |
| Mandarin Chinese | Standard | /t/ | Pinyin romanization | |
| English | /d/ | |||
| French | /d/ | Sometimes silent word-finally | ||
| German | /d/, /t/ | See German orthography | ||
| Portuguese | /d/ | |||
| Spanish | /d/ | |||
| Turkish | /d/ | |||
English
In English, ⟨d⟩ generally represents the voiced alveolar plosive /d/.
D is the tenth most frequently used letter in the English language.
Other languages

In most languages that use the Latin alphabet, ⟨d⟩ generally represents the voiced alveolar or voiced dental plosive /d/.
In the Vietnamese alphabet, it represents the sound /z/ in northern dialects or /j/ in southern dialects. (See D with stroke and Dz (digraph).)
In Fijian it represents a prenasalized stop /ⁿd/.
In some languages where voiceless unaspirated stops contrast with voiceless aspirated stops, ⟨d⟩ represents an unaspirated /t/, while ⟨t⟩ represents an aspirated /tʰ/. Examples of such languages include Icelandic, Scottish Gaelic, Navajo and the Pinyin transliteration of Mandarin.
Other systems
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, ⟨d⟩ represents the voiced alveolar plosive /d/.
Other uses
- In the hexadecimal (base 16) numbering system, D is a number that corresponds to the number 13 in decimal (base 10) counting.
- The Roman numeral D represents the number 500.
- Unit prefix d, meaning one tenth.
- D is the grade below C but above E/F in the school grading system.
- D is the International vehicle registration code for Germany (see also .de).
- In Cantonese: Because the lack of Unicode CJK support in early computer systems, many Hong Kongers and Singaporeans used the capitalized D to represent 啲 (lit. a little).
- In the Gregory-Aland system for cataloging Biblical manuscripts, D can refer to documents in the Western text-type tradition, either Codex Bezae or Codex Claromontanus.
- d. is the standard abbreviation for the Penny (British pre-decimal coin) (from Latin: denarius)
Related characters
Descendants and related characters in the Latin alphabet
- Ɖ ɖ : African D
- Ð ð : Latin letter Eth
- D with diacritics: Đ đ Ꟈ ꟈ Ɗ ɗ Ḋ ḋ Ḍ ḍ Ḑ ḑ Ḓ ḓ Ď ď Ḏ ḏ
- Phonetic symbols related to D:
- Symbols related to D used in the IPA: ɖ ɗ
- Symbols related to D used in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet: ᴅ ᴰ ᵈ
- Superscript IPA letters: 𐞋 𐞌 𐞍
- Other phonetic symbols related to D: ȡ ᵭ ᶁ ᶑ
- Ƌ ƌ : D with topbar
- 𝼥 : D with mid-height left hook - Used by the British and Foreign Bible Society in the early 20th century for romanization of the Malayalam language.
- Ꝺ ꝺ : Insular D is used in various phonetic contexts
Ancestors and siblings in other alphabets
- 𐤃 : Semitic letter Dalet, from which the following symbols originally derive
Derived signs, symbols and abbreviations
- ₫ : Đồng sign
- ⅆ : Unicode symbol for d used as derivative symbol
- ∂ : the partial derivative symbol,
Other representations
Computing
The Latin letters ⟨D⟩ and ⟨d⟩ have Unicode encodings U+0044 D LATIN CAPITAL LETTER D and U+0064 d LATIN SMALL LETTER D. These are the same code points as were used in ASCII and ISO 8859. There are also precomposed character encodings for ⟨D⟩ and ⟨d⟩ with diacritics, for most of those listed above; the remainder are produced using combining diacritics.
Variant forms of the letter have unique code points for specialist use: the alphanumeric symbols set in mathematics and science, plosive sounds in linguistics, and halfwidth and fullwidth forms for legacy CJK font compatibility.
Other
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Delta | ⓘ |
 |
|  |  | 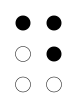 |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual alphabet (ASL fingerspelling) | British manual alphabet (BSL fingerspelling) | Braille dots-145 Unified English Braille |
In British Sign Language (BSL), the letter 'd' is indicated by signing with the right hand held with the index and thumb extended and slightly curved, and the tip of the thumb and finger held against the extended index of the left hand.
References
External links

This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article D, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.


