Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral and one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), the others being calcite and vaterite.
It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments.
| Aragonite | |
|---|---|
 Aragonite from Los Molinillos, Cuenca, Spain, sample width about 4 cm | |
| General | |
| Category | Carbonate minerals |
| Formula (repeating unit) | CaCO3 |
| IMA symbol | Arg |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Unit cell | l a = 4.9598(5) Å, b = 7.9641(9) Å, and c = 5.7379(6) Å at 25 °C |
| Identification | |
| Color | Can come in a variety of colors, but commonly red or white |
| Crystal habit | Commonly dendritic or pseudo-hexagonal; can also be acicular, tabular, prismatic, coral-like |
| Twinning | Cyclic on {110}, forms pseudohexagonal aggregates. If polysynthetic, forms fine striations parallel to [110]. |
| Cleavage | Good on [110], Poor on {110}. |
| Fracture | Subconchoidal |
| Tenacity | Very brittle |
| Mohs scale hardness | 3.5–4 |
| Luster | Vitreous, waxy, resinous |
| Streak | White |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent to opaque |
| Specific gravity | 2.94 |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (−) |
| Refractive index | nω = 1.550 nε = 1.650 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.155 |
| 2V angle | Measured 18–19° |
| Dispersion | Weak |
| Extinction | Parallel |
| Ultraviolet fluorescence | Faint white-blue to blue-violet |
| Solubility | Soluble in acids, and saltwater (but takes longer) |
| Common impurities | Commonly strontium, zirconium, lead |
| Other characteristics | Thermodynamically unstable, Morphs slowly back into calcite |
| References | |

The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called flos-ferri ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines.
Occurrence
The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of aragonite deposit is very common in Spain, and there are also some in France.
An aragonite cave, the Ochtinská Aragonite Cave, is situated in Slovakia.
In the US, aragonite in the form of stalactites and "cave flowers" (anthodite) is known from Carlsbad Caverns and other caves. For a few years in the early 1900s, aragonite was mined at Aragonite, Utah (now a ghost town).
Massive deposits of oolitic aragonite sand are found on the seabed in the Bahamas.

Aragonite is the high pressure polymorph of calcium carbonate. As such, it occurs in high pressure metamorphic rocks such as those formed at subduction zones.
Aragonite forms naturally in almost all mollusk shells, and as the calcareous endoskeleton of warm- and cold-water corals (Scleractinia). Several serpulids have aragonitic tubes. Because the mineral deposition in mollusk shells is strongly biologically controlled, some crystal forms are distinctively different from those of inorganic aragonite. In some mollusks, the entire shell is aragonite; in others, aragonite forms only discrete parts of a bimineralic shell (aragonite plus calcite). The nacreous layer of the aragonite fossil shells of some extinct ammonites forms an iridescent material called ammolite.
Aragonite also forms naturally in the endocarp of Celtis occidentalis.
The skeleton of some calcareous sponges is made of aragonite.[citation needed]
Aragonite also forms in the ocean inorganic precipitates called marine cements (in the sediment) or as free crystals (in the water column). Inorganic precipitation of aragonite in caves can occur in the form of speleothems. Aragonite is common in serpentinites where magnesium-rich pore solutions apparently inhibit calcite growth and promote aragonite precipitation.
Aragonite is metastable at the low pressures near the Earth's surface and is thus commonly replaced by calcite in fossils. Aragonite older than the Carboniferous is essentially unknown.
Aragonite can be synthesized by adding a calcium chloride solution to a sodium carbonate solution at temperatures above 60 °C (140 °F) or in water-ethanol mixtures at ambient temperatures.
Physical properties
Aragonite is a thermodynamically unstable phase of calcium carbonate at any pressure below about 3,000 bars (300,000 kPa) at any temperature. Aragonite nonetheless frequently forms in near-surface environments at ambient temperatures. The weak Van der Waals forces inside aragonite give an important contribution to both the crystallographic and elastic properties of this mineral. The difference in stability between aragonite and calcite, as measured by the Gibbs free energy of formation, is small, and effects of grain size and impurities can be important. The formation of aragonite at temperatures and pressures where calcite should be the stable polymorph may be an example of Ostwald's step rule, where a less stable phase is the first to form. The presence of magnesium ions may inhibit calcite formation in favor of aragonite. Once formed, aragonite tends to alter to calcite on scales of 107 to 108 years.
The mineral vaterite, also known as μ-CaCO3, is another phase of calcium carbonate that is metastable at ambient conditions typical of Earth's surface, and decomposes even more readily than aragonite.
Uses
In aquaria, aragonite is considered essential for the replication of reef conditions. Aragonite provides the materials necessary for much sea life and also keeps the pH of the water close to its natural level, to prevent the dissolution of biogenic calcium carbonate.
Aragonite has been successfully tested for the removal of pollutants like zinc, cobalt and lead from contaminated wastewaters.
Claims that magnetic water treatment can reduce scaling, by converting calcite to aragonite, have been met with skepticism, but continue to be investigated.
Gallery
- Aragonite crystals from Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha, Spain
- Aragonite crystal cluster from Spain
- Remnant biogenic aragonite (thin, rainbow-colored shell) on the ammonite Baculites (Pierre Shale, Late Cretaceous, South Dakota)
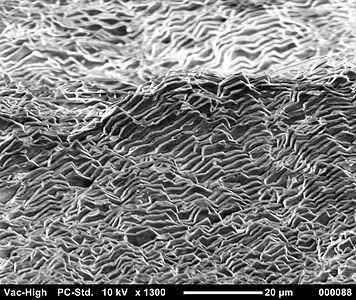
- Scanning electron microscope image of aragonite layers in the nacre of a blue mussel (Mytilus edulis)
- Fluorescence of aragonite
See also
- Aragonite sea
- Ikaite, CaCO3·6H2O
- List of minerals
- Monohydrocalcite, CaCO3·H2O
- Nacre, otherwise known as "Mother-of-Pearl"
References
External links
This article uses material from the Wikipedia English article Aragonite, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license ("CC BY-SA 3.0"); additional terms may apply (view authors). Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
®Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wiki Foundation, Inc. Wiki English (DUHOCTRUNGQUOC.VN) is an independent company and has no affiliation with Wiki Foundation.